Table of Content

Have you ever worked on a project where everything looked perfect on paper, but reality became late for feedback, rework and frustrated teammates? That is exactly why understanding What is Agile Methodology is important. Agile helps teams adapt quickly, learn continuously, and deliver value faster without waiting until the final deadline.
In this blog, you will explore What is Agile Methodology in detail including how it works, its types, principles, pillars, life cycle and the key benefits and drawbacks. This will help you use Agile more effectively and improve how your team delivers results.
What is Agile Methodology?
Agile Methodology is a flexible, iterative approach to Project Management and Software Development. Unlike traditional methods that follow a strict, step-by-step process, Agile breaks projects into smaller, manageable tasks called iterations or sprints. This allows teams to focus on delivering parts of the project quickly and efficiently.
Agile encourages collaboration, regular feedback, and adaptability. Teams continuously gather customer input and make improvements along the way, ensuring the final product meets evolving needs. This method helps deliver high-quality results faster while staying responsive to change.
How Does the Agile Methodology Work?
Agile Methodology works through short, repeatable cycles, which are called sprints or iterations, that last for one to four weeks. Each sprint involves planning, developing, testing, and reviewing a small part of the project. Teams set clear goals for each sprint and work together daily to track progress, solve issues, and stay aligned.
Here’s How it Functions:
1) Plan the Sprint: The team decides which tasks or features to work on.
2) Develop and Test: They build and test the chosen features during the sprint.
3) Daily Stand-ups: Short daily meetings keep everyone updated and aligned.
4) Review and Demo: At the end, the team reviews the work and demonstrates it to stakeholders.
5) Retrospective: The team reflects on what went well and what can be improved.
This loop repeats, which allows the team to adapt quickly to feedback and changing requirements. It ensures the final result meets the user's needs efficiently for better results.
Types of Agile Methodologies
Agile is a family of flexible and adaptive frameworks that offer a unique approach to planning, executing, and delivering projects. Here are some of the most popular types:
1) Kanban
Kanban is a visual Workflow Management approach that focuses on real-time communication and task tracking. It uses boards with columns like do, in progress or done to help teams visualise work, limit work-in-progress, and improve flow. There are no fixed iterations, so tasks move fluidly based on team capacity. It’s ideal for continuous delivery and operational teams.

Key Highlights:
1) Visual task management
2) Limits work-in-progress
3) Continuous improvement
4) No set roles or time frames
Start your Project Management career with our Introduction to Project Management Training for a solid foundation!
2) Scrum
Scrum is one of the most commonly used Agile methods. It breaks projects into short cycles called sprints, usually two to four weeks. It includes roles like Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team. Daily stand-up meetings and sprint reviews ensure transparency and adaptability.
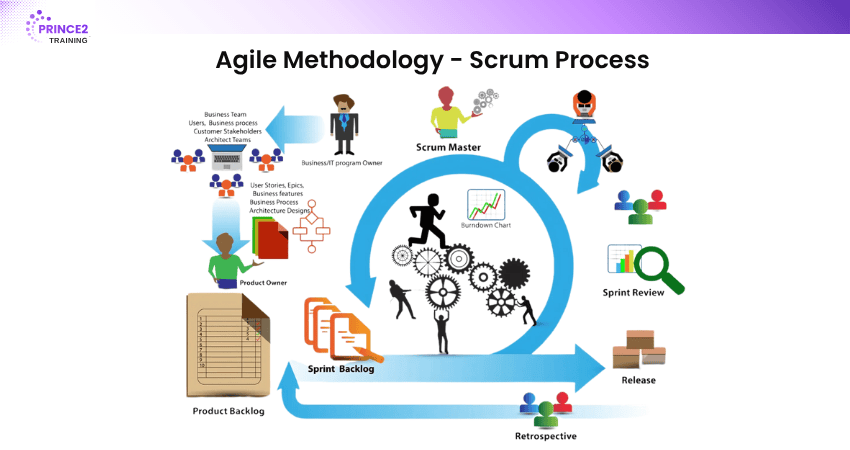
Key Highlights:
1) Time-boxed sprints
2) Defined team roles
3) Product backlog prioritisation
4) Frequent reviews and retrospectives
3) Extreme Programming (XP)
Extreme Programming (XP) is focused on improving software quality and responsiveness. It promotes technical excellence through practices like pair programming, test-driven development (TDD), continuous integration, and frequent releases. XP is best for projects with changing requirements and tight deadlines.
Key Highlights:
1) Frequent releases
2) Test-driven development
3) Simple design and continuous feedback
4) High coding standards
4) Adaptive Project Framework (APF)
APF is designed to handle projects with unclear or constantly changing requirements. It encourages iterative planning and feedback loops to refine objectives along the way. Stakeholders are closely involved, and goals may evolve throughout the project.
Key Highlights:
1) Adaptable and flexible
2) High stakeholder involvement
3) Continuous learning and refinement
4) Value-driven delivery
5) Feature Driven Development (FDD)
FDD is a model-driven, short and structured process focused on delivering tangible features every few days. It begins with a broad model, followed by feature lists, planning, designing, and building by feature. It’s ideal for large teams working on complex systems.
Key Highlights:
1) Feature-focused planning
2) Scalable for big projects
3) Emphasis on design and code quality
4) Structured but flexible
6) Extreme Project Management (XPM)
XPM is built for chaotic and rapidly changing environments. It embraces uncertainty and uses short planning cycles to make constant adjustments. Rather than controlling the project, XPM guides it based on discovery and learning.
Key Highlights:
1) Embraces change and risk
2) Suitable for experimental projects
3) Encourages creativity and innovation
4) Focus on flexibility over structure
7) Adaptive Software Development (ASD)
ASD is ideal for complex software projects where requirements change frequently. It focuses on rapid delivery through three phases: speculate, collaborate, and learn. It values learning from each iteration and adapting the approach accordingly.
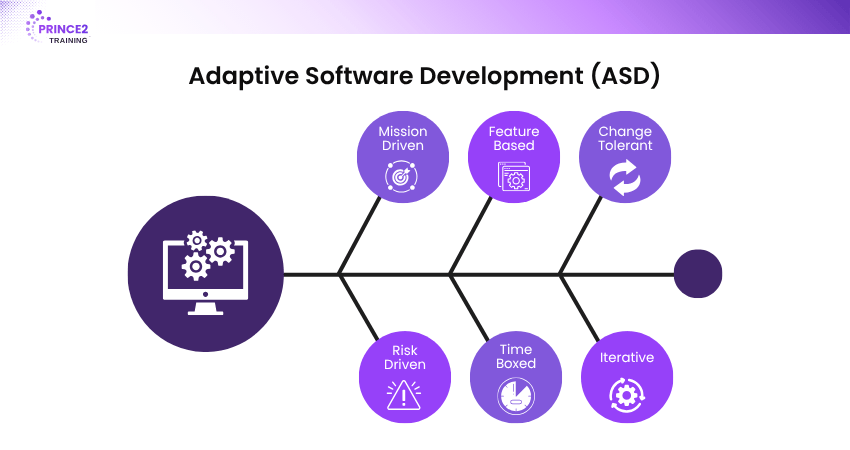
Key Highlights:
1) Encourages innovation and flexibility
2) Emphasises learning over rigid planning
3) Focus on teamwork and rapid delivery
4) Useful for uncertain or emerging technologies
8) Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM)
DSDM is a disciplined Agile method with strong governance and user involvement. It has fixed time and cost constraints but allows for scope flexibility. It suits projects needing formal standards, like government or enterprise-level work.
Key Highlights:
1) Fixed cost and time, flexible scope
2) High user engagement
3) Strong project governance
4) Ideal for regulated industries
Build core Agile project knowledge for success with our PRINCE2 Agile® Foundation Training now!
What are the 12 Agile Principles?
The 12 Agile Principles provide a foundation for effective, flexible, and value-driven project delivery. Here are the principles explained clearly and concisely:
1) Customer Satisfaction: Deliver valuable work early and consistently so customers experience meaningful benefits throughout the project.
2) Welcome Changing Requirements: Respond positively to new or evolving needs to ensure the final outcome stays relevant and effective.
3) Frequent Delivery: Release working outputs in short, regular cycles to gather feedback quickly and adapt when necessary.
4) Daily Collaboration: Encourage ongoing communication between teams and business stakeholders to maintain alignment and clarity.
5) Motivated Individuals: Provide capable people with trust, support and the right environment so they can perform at their best.
6) Face-to-Face Communication: Use direct conversation to reduce misunderstanding and improve knowledge sharing within the team.
7) Working Outputs as Progress: Measure success based on what is functional and usable rather than on documentation or plans.
8) Sustainable Pace: Maintain a steady work rhythm that teams can uphold long-term without sacrificing quality.
9) Technical Excellence: Prioritise strong engineering practices and thoughtful design to keep the product adaptable and maintainable.
10) Simplicity: Remove unnecessary work and concentrate on features and tasks that genuinely add value.
11) Self-organising Teams: Allow teams to decide how work is completed, promoting creativity and shared responsibility.
12) Regular Reflection: Review performance at frequent intervals and adjust behaviours or processes to improve effectiveness.
What are the Four Pillars of Agile?
Agile outlines four core values that guide all practices on delivering value, adapting to change, and prioritising people and collaboration over rigid systems.
Individuals Over Processes and Tools
1) People are the heart of Agile success.
2) People and interactions drive success more than tools or rules
3) Strong teamwork and communication matter most
4) Tools support the process but don’t replace human input
Working Software Over Comprehensive Documentation
1) It aims to deliver value through functional products.
2) Deliver usable features instead of lengthy paperwork
3) Focus on creating real value for users
4) Documentation is kept light and relevant
Customer Collaboration Over Contract Negotiation
1) Strong relationships matter more than fixed ones.
2) Work closely with customers throughout the project
3) Adapting to their feedback instead of sticking rigidly to contracts
4) Build stronger relationships and better products
Responding to Change Over Following a Plan
1) Being flexible means sticking to outdated plans.
2) Embrace change, even late in development
3) Stay flexible and adjust to new needs or priorities
4) Plans guide the project but don’t restrict it
Elevate your career with our PRINCE2 Agile® Practitioner Training and excel in dynamic project environments
Life Cycle of Agile Methodology
Agile Methodology follows a dynamic and repetitive life cycle that focuses on continuous improvement, collaboration, and flexibility. Instead of following a strict linear path, it loops through phases repeatedly and delivers working software after each cycle. Let's discuss the life cycle of this methodology:
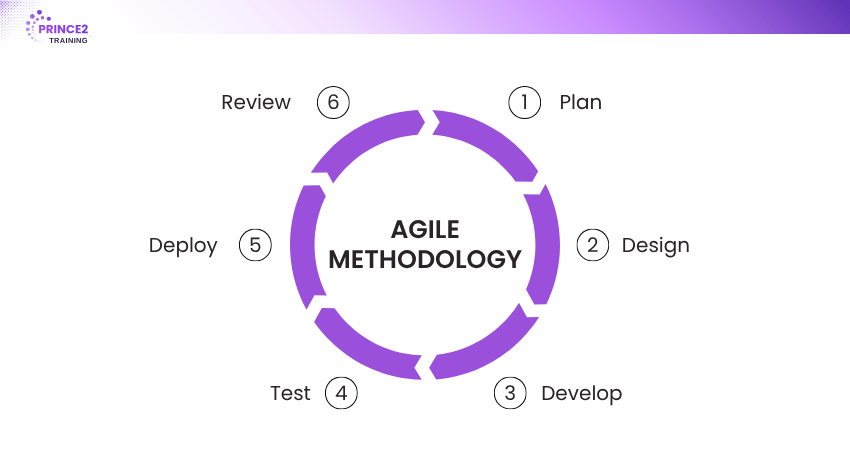
Requirement Gathering
This is the starting point of the Agile lifecycle. The team collaborates with stakeholders to understand what needs to be done. They gather the requirements in the form of user stories that are short, simple descriptions of a feature from the user’s perspective.
Key Activities Include:
1) Identify project goals and user needs
2) Break down features into user stories
3) Prioritise backlog items based on value and urgency
4) Prepare for sprint planning
Design
Once requirements are defined, the design phase begins. Agile doesn’t focus on detailed documentation but works on just enough design to guide development. It emphasises simplicity and flexibility and allows designs to evolve.
Key Activities:
1) Sketch wireframes or mockups
2) Define UI/UX flows and architecture
3) Collaborate with developers for technical feasibility
4) Ensure designs align with sprint goals
Deployment
This development phase is where actual coding happens. Developers pick tasks from the sprint backlog and build the features. Work is done in short cycles and allows the team to make frequent updates and testing.
Key Activities:
1) Write clean, testable code
2) Use pair programming or collaborative coding
3) Implement small and functional parts of the system
4) Ensure each feature is production-ready
Testing
Agile integrates testing into every sprint, not just at the end. Continuous testing helps catch bugs early and ensures the product is always in a releasable state. Test-driven Development (TDD) is often used.
Key Activities:
1) Perform unit, integration, and user testing
2) Automated and manual testing included
3) Log bugs and fix them within the sprint
4) Validate features against user stories
Development (Coding)
After features pass testing, they are deployed, sometimes daily or weekly. Agile encourages frequent, smaller releases so users can see progress and provide feedback sooner.
Key Activities:
1) Deploy to staging or production environments
2) Use CI/CD pipelines for automation
3) Release new features incrementally
4) Monitor for issues post-deployment
Review (Maintenance)
This is the reflection and maintenance stage. The team holds a sprint review and a retrospective to evaluate what worked, what didn’t, and how to improve in the next cycle. Maintenance involves fixing post-release bugs and enhancing features.
Key Activities:
1) Review completed work with stakeholders
2) Collect feedback for improvement
3) Conduct retrospectives for team learning
4) Tackle maintenance and optimisation tasks
Achieve recognised project leadership by registering for our best PRINCE2® Practitioner Training today!
Advantages of Agile Development Methodology
Agile offers a wide range of advantages that drive better outcomes for businesses, teams, and customers.
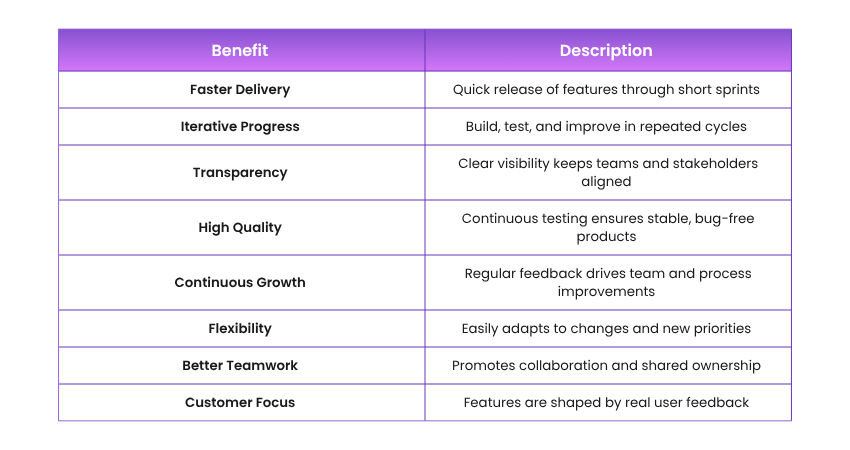
Faster Delivery
Agile promotes faster delivery by breaking projects into smaller, manageable tasks. Teams can quickly develop, test, and release functional features, allowing stakeholders to see results sooner and providing opportunities for early feedback and timely adjustments.
Iterative Development
Agile uses short, repetitive development cycles called sprints. This allows teams to constantly refine and improve the product, making it easier to adapt to changes and deliver incremental value throughout the project life cycle.
Transparency
Agile encourages open communication and regular progress updates through daily stand-ups, sprint reviews, and visual boards. This ensures all team members and stakeholders are aligned, aware of project status, and involved in decision-making.
Quality Assurance
Testing is integrated into every sprint in Agile, allowing for continuous validation of the product. Frequent reviews and early bug detection help maintain high-quality standards and ensure that each feature meets the required specifications.
Continuous Improvement
Agile supports continuous improvement through regular retrospectives where teams reflect on what worked and what didn’t. This ongoing learning helps enhance processes, strengthen collaboration, and improve overall project performance over time.
Agile Methods are Adaptable
Agile methods easily adapt to changing project requirements. Teams can adjust priorities, shift focus, and embrace new ideas quickly, ensuring the final product stays relevant and aligned with evolving customer and business needs.
Start leading high-impact projects – Our Introduction to Project Management Training opens the door. Join today!
Agile Fosters Collaborative Teamwork
Agile builds a strong culture of teamwork by encouraging collaboration among cross-functional teams. Developers, testers, designers, and stakeholders work closely together, ensuring better communication, faster problem-solving, and shared ownership of project success.
Agile Methods Focus on Customer Needs
Agile keeps the customer at the centre of development by gathering feedback early and often. This customer-focused approach ensures that the delivered product meets real-world needs and provides maximum value to end users.
Disadvantages of Agile Methodology
While Agile offers many advantages, it’s not a perfect fit for every project or organisation. Here are some of its limitations:
1) High customer involvement is needed, which may not always be possible
2) Hard to predict timelines and costs due to ongoing changes
3) Not ideal for inexperienced or rigid teams
4) Minimal documentation can cause issues in maintenance or compliance
5) The risk of scope becomes high if changes aren’t controlled properly
6) Less suited for regulated or large-scale projects
7) Requires cultural and mindset shifts, which can face resistance
Conclusion
Agile continues to shape how modern teams deliver products with speed, flexibility and strong customer focus. Understanding What is Agile Methodology gives professionals the tools to embrace change, improve collaboration and deliver value that truly matters. Whether you are new to Agile or looking to refine your approach, adopting its principles can transform how your team works and succeed in today’s fast-moving world.
Gain globally recognised Project Management expertise for success with industry-leading PRINCE2 Training today!
 Contact@prince2training.co.uk
Contact@prince2training.co.uk 01344203999
01344203999





 Back
Back







 Continue Browsing
Continue Browsing
