Table of Content


Have you ever worked on a project where one missed step caused everything to fall apart? Maybe a product launch is waiting on approvals or a client task is blocking all progress. In moments like these, you want order and clarity. That is why many teams still trust the Waterfall Methodology. It works like a clear instruction guide, where each step builds smoothly on the one before it.
In this blog, you will explore What is Waterfall Methodology, learn its six phases, and understand its advantages and disadvantages. You will also review a simple Waterfall example so you can relate it to real projects. Let’s begin
Table of Contents
1) What is Waterfall Methodology?
2) What are the Stages of the Waterfall Methodology?
3) When to Use the Waterfall Methodology?
4) Advantages of the Waterfall Methodology
5) Disadvantages of the Waterfall Methodology
6) Waterfall Methodology Example
7) How Does the Waterfall Methodology Vary by Industry?
8) Conclusion
What is Waterfall Methodology?
The Waterfall Methodology is a sequential and structured approach to Project Management. It follows a linear progression, where each stage is dependent on the completion of the previous one. This model was introduced by Dr. Winston W. Royce in 1970 as a framework for Software Development. Its disciplined approach has made it applicable across various industries, including construction, healthcare, and manufacturing.
Unlike Agile, which embraces change and iterative progress, Waterfall relies on a fixed plan with well-defined objectives. Once a phase is completed, teams cannot return to modify it without starting over, making it important to get each step right from the beginning.
The key characteristics of the Waterfall Methodology include:
1) Strict Sequential Flow: The project moves in a set order from one phase to another.
2) Detailed Documentation: Every step and requirement is documented before execution.
3) Little to no Client Involvement After Planning: Clients provide requirements at the beginning, and the project progresses without much feedback until delivery.
4) Clear Deliverables: Each phase must be completed before progressing, ensuring structured development.
Now, let’s break down the six key phases of the Waterfall Methodology

What are the Stages of the Waterfall Methodology?
Now, let us look at the six Waterfall Methodology Phases for Project Management:
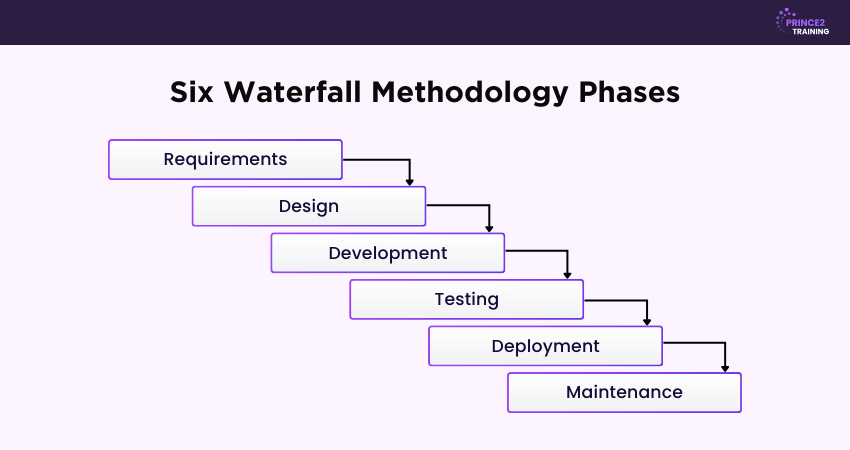
1) Requirements
Every great project starts with a solid plan. In this phase, the project team gathers all the requirements from stakeholders, clients, or end-users. This includes defining the project’s scope, objectives, deliverables, and constraints. This phase is crucial because any misunderstanding or missing detail can cause major issues later.
The requirements phase includes:
1) Conducting stakeholder meetings
2) Collecting technical and functional requirements
3) Documenting expected outcomes
4) Defining project scope and budget constraints
5) Identifying potential risks and mitigation strategies
6) Establishing project timelines and milestones
Unlike Agile, where requirements can evolve, Waterfall is locked in after this phase, so getting it right is critical!
2) Design
With the requirements in place, it's time to create the blueprint. Teams work on system architecture, user interface designs, databases, and workflows in this phase. This is where technical and design specifications are created for the development team to follow.
Key activities in this phase include:
1) Creating technical specifications
2) Designing system architecture
3) Developing wireframes or blueprints
4) Selecting the technology stack
5) Identifying required third-party integrations
6) Establishing security and compliance measures
If the project were a house, this would be the stage where architects and engineers draft the floor plan and determine materials. There’s no room for improvisation later, so every detail must be mapped out precisely.
3) Development
Once the design is approved, the actual building begins. Developers create the product or system strictly according to the predefined specifications. Waterfall treats development as one complete phase rather than breaking it into iterative cycles.
The development phase includes:
1) Coding all system components
2) Integrating features as defined in the design
3) Building databases and interfaces
4) Following coding standards and documentation
5) Preparing the system for testing
6) Ensuring feature completion before testing begins
4) Testing
After development, the entire system is tested to identify defects, verify requirements and ensure proper functioning. This phase checks for usability, performance and overall stability.
The testing phase includes:
1) Unit and integration testing
2) System testing
3) Debugging and error fixing
4) Quality assurance checks
5) Performance and load testing
6) Validating requirements compliance
Since testing happens after full development, late-found issues can be costly.
5) Deployment
This phase involves releasing the completed product into a real-world environment. Deployment activities ensure the system is properly installed, configured and ready for end-users.
Key deployment activities include:
1) Installing or launching the system
2) Conducting user training
3) Final system integration
4) Monitoring initial system behaviour
5) Collecting user feedback for minor adjustments
6) Ensuring stability during rollout
6) Maintenance
Even after a project is completed, maintenance is always needed. Bugs may arise, updates may be required, or user feedback might require minor tweaks. This is the phase where ongoing support is provided to ensure the system continues functioning smoothly.
Maintenance activities include:
1) Bug fixes and patches
2) System updates
3) User support and troubleshooting
4) Performance optimisation for better efficiency
5) Implementing security enhancements
6) Scaling the system as per business growth
Validate your advanced Project Management skills with precision. Join our PRINCE2® Practitioner Training now!
When to Use the Waterfall Methodology
Waterfall isn’t ideal for every project, but it works best in structured environments where planning and predictability are key. It is most effective when:
1) Clear and Fixed Objectives: The project scope, goals, and deliverables are well-defined.
2) Stable Requirements: Minimal expected changes, ensuring each phase can progress without rework.
3) Strict Budget and Timeline Adherence: Works well when cost and deadlines are firmly set, with no flexibility for iteration.
4) Regulatory and Compliance-Driven Projects: Industries like healthcare, aerospace, and finance require detailed documentation and approval at each stage.
5) Mission-critical Systems: Used where failures are costly or unacceptable, such as in banking systems, defence, and infrastructure projects.
6) Repeatable Workflows: Ideal for structured processes like manufacturing, where the same steps are followed consistently.
7) Large-scale Projects with Multiple Teams: Ensures smooth coordination in projects requiring extensive planning and documentation.
8) New Employee Training and Onboarding: Works well for structured training programmes with predefined steps.
The Waterfall is most effective when precision, control, and documentation are crucial to success.
Advantages of the Waterfall Methodology
Waterfall gives a structured, step-by-step project flow. Each phase has clear tasks, making planning and tracking easier. With early planning, the project stays stable and predictable. Here are its key advantages:
1) Clear and Organised Project Structure
Waterfall follows a step-by-step flow where each stage has set goals and tasks. Teams move from requirements to design, development, testing and maintenance. Since plans are fixed at the start, the project moves in a clear and predictable way.
2) Seamless Information Handover
Every stage creates its own deliverables and documentation. This makes it easy to pass information to the next stage. Team members can understand what was completed earlier, and support teams can continue the work without confusion.
3) Simple and Straightforward Management
Since each stage has set goals and must be finished before moving ahead, tracking progress becomes easy. Managers can see where the project stands and quickly notice any delays or problems.
4) Strong Focus on Early Planning
At the beginning, teams spend time defining the requirements and project goals. This planning helps everyone understand what needs to be done and how the work will move forward with clarity.
5) Highly Stable Project Framework
Waterfall uses a fixed and linear process, which keeps the project stable. Once the requirements are decided, they do not change much. This makes it easier to work confidently and predict challenges during the project.
Disadvantages of the Waterfall Methodology
Waterfall offers structure, but it can be rigid. Changes are hard to manage, and issues often surface late in the process. Here are the main disadvantages to keep in mind:
High Cost and Limited Flexibility
Waterfall requires all requirements to be decided at the start. If changes are needed later, they can be expensive and difficult to manage. The process does not adjust easily once the project begins.
Minimal Scope for Revision or Improvement
Since each stage must be completed before moving to the next, there is very little room to review or improve earlier work. If something needs to be corrected, the team may need to go back several steps.
Lacks Focus on the Client or End User
Clients usually see the final result only at the end of the project. This reduces chances for feedback during development, which may lead to a product that does not meet user expectations.
Testing Occurs Late in the Process
In Waterfall, testing happens only after development is finished. This means errors are found late, and fixing them at that stage can take more time and effort for teams to manage effectively.
Gain powerful project skills recognised across industries with our PRINCE2 Foundation & Practitioner Training – Join now!
Waterfall Methodology Example
Imagine a construction project for a new office building. The Waterfall Methodology works perfectly here because:
1) Requirements: All building needs, blueprints and specifications are defined upfront.
2) Design: Architects create detailed structural, electrical and interior plans.
3) Development: Engineers and contractors prepare materials, schedules and construction frameworks.
4) Testing: Safety checks, material quality tests and regulatory inspections are carried out before full construction continues.
5) Deployment: The building is constructed, fitted out and handed over for use.
6) Maintenance: Ongoing building management, repairs and updates are handled post-handover.
How Does the Waterfall Methodology Vary by Industry?
Waterfall varies across industries based on project needs and flexibility. The core step-by-step flow stays the same, but its use changes with the stability of requirements. Here is how it applies in different industries:
Waterfall in Software Development
Waterfall suits software projects with clear, stable requirements like government or internal systems. The V Model adds testing at each stage, and Incremental models offer some flexibility. A key limitation is that errors appear late and changes are difficult to manage later.
Waterfall for B2B
B2B projects often have long timelines and fixed deliverables, so Waterfall helps teams stay organised and aligned. It works well when tasks are clear, but it can be limiting if a project needs regular feedback from clients.
Waterfall for B2C
Waterfall can support large B2C projects where the product is well-defined from the beginning, such as hardware or major software releases. The challenge is that consumer trends can change quickly, and Waterfall makes it difficult to adjust once the project has started.
Conclusion
Waterfall Methodology provides a clear and organised way to manage projects with stable requirements and predictable outcomes. Its structured flow helps teams plan well and maintain steady progress. Although it is less flexible for changing needs, it remains effective for well-defined work. Choosing the right approach depends on how stable your project requirements are.
Advance your project career through our PRINCE2 Training and develop strong professional credibility
 Contact@prince2training.co.uk
Contact@prince2training.co.uk 01344203999
01344203999





 Back
Back






 Continue Browsing
Continue Browsing
