Table of Content


One unexpected cyberattack, a missed compliance deadline, or a supplier delay can cause even a thriving business to stumble. Risks don’t wait for readiness, but a strong Risk Management Process ensures you're prepared. It helps identify threats early, assess their potential impact, and implement strategies to minimise damage and seize opportunities.
In this blog, we’ll walk you through what the Risk Management Process is, its strategies, and real-world examples to help you strengthen your organisation’s resilience and decision-making. Let’s get started!
What is the Risk Management Process?
The Risk Management Process is a structured approach for identifying, assessing, prioritising, and mitigating risks that may impact an organisation. It helps in reducing uncertainties, enhances decision-making, and strengthens overall business resilience. Effective Risk Management ensures that organisations can anticipate potential threats. This allows them to implement proactive measures to minimise disruptions.
Risks can stem from various internal and external factors that challenge organisational stability. These include financial instability, regulatory changes, cybersecurity threats, and operational inefficiencies. These factors can lead to significant financial and reputational damage without proper Risk Management. Addressing risks systematically enables organisations to create robust contingency plans.
Organisations can safeguard their objectives and ensure long-term sustainability by systematically addressing risks. A proactive Risk Management approach fosters confidence among stakeholders and promotes stability. It also enables businesses to adapt to evolving challenges and remain competitive. Through continuous monitoring and improvement, organisations can navigate uncertainties effectively.
Why is Risk Management Important?
A well-implemented Risk Management strategy allows businesses to effectively identify, assess, and mitigate risks. By doing so, organisations can strengthen their ability to navigate uncertainties and sustain long-term growth. Proactive Risk Management fosters confidence among stakeholders and ensures compliance with industry regulations.
1) Improve decision-making by providing risk-informed insights
2) Reduce financial losses by proactively addressing potential threats
3) Ensure regulatory compliance by aligning with industry standards
4) Enhance business continuity through mitigation strategies
5) Strengthen stakeholder confidence by demonstrating responsible governance
6) Foster long-term sustainability by adapting to evolving challenges
5 Steps for Risk Management Process
The Risk Management Process follows a structured five-step approach, ensuring risks are managed effectively and proactively.
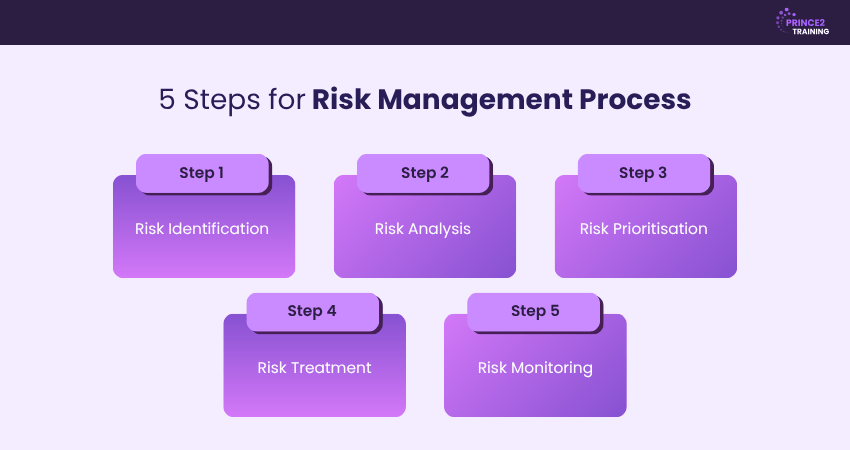
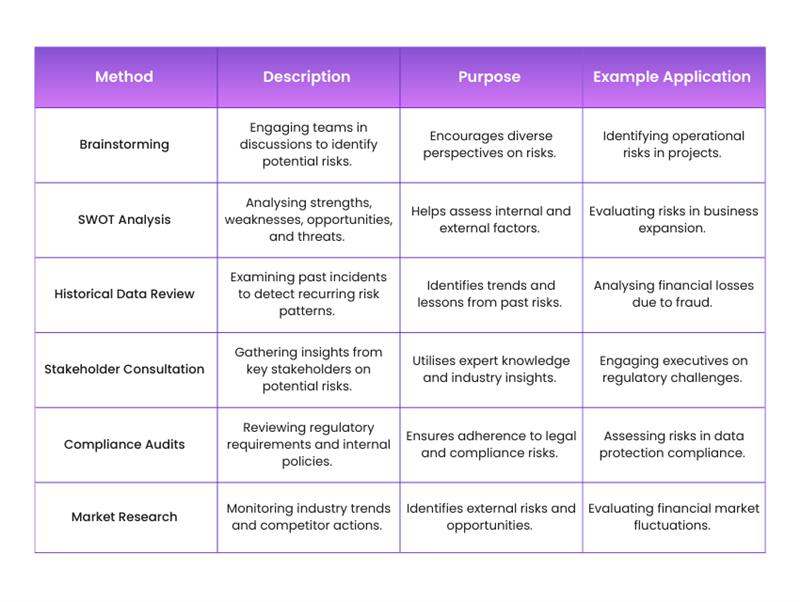
Step 1: Risk Identification
1) Identify potential risks affecting business operations, finances, and compliance
2) Use brainstorming sessions to explore possible threats
3) Conduct a SWOT analysis to assess strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats
4) Review historical data to detect recurring risk patterns
5) Consult stakeholders to gain insights into hidden risks
6) Document identified risks for further analysis and management
Become a Certified Project Management Expert – Join PRINCE2® Foundation & Practitioner Today!
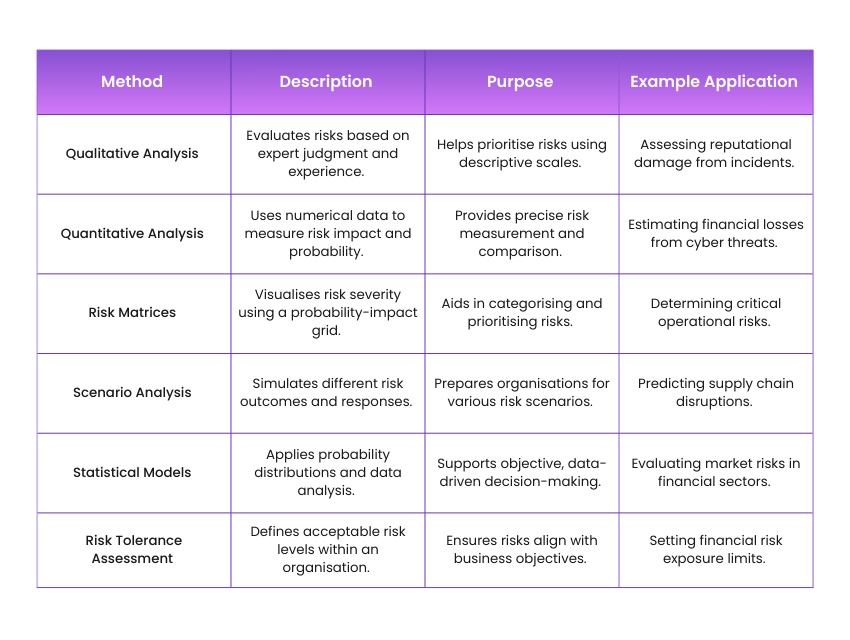
Step 2: Risk Analysis
1) Assess the potential impact and likelihood of identified risks
2) Use qualitative and quantitative evaluation methods
3) Apply risk matrices to visualise risk severity
4) Conduct scenario analysis to predict potential consequences
5) Employ statistical models for data-driven risk assessments
6) Determine the organisation’s risk tolerance levels
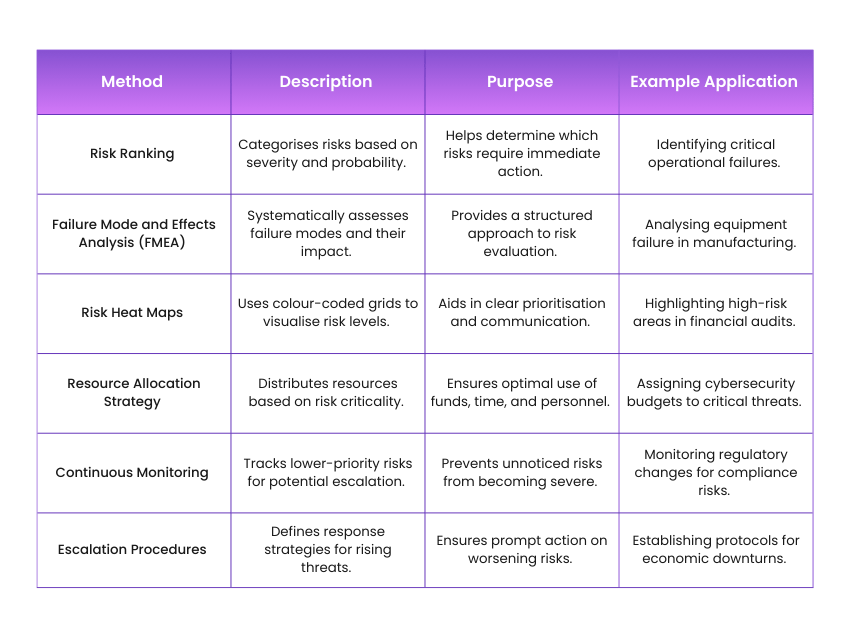
Step 3: Risk Prioritisation
1) Rank risks based on severity and likelihood
2) Address high-priority risks with immediate action
3) Monitor lower-priority risks for potential escalation
4) Utilise Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) for structured prioritisation
5) Apply risk heat maps for clear risk visualisation
6) Allocate resources efficiently to manage critical risks
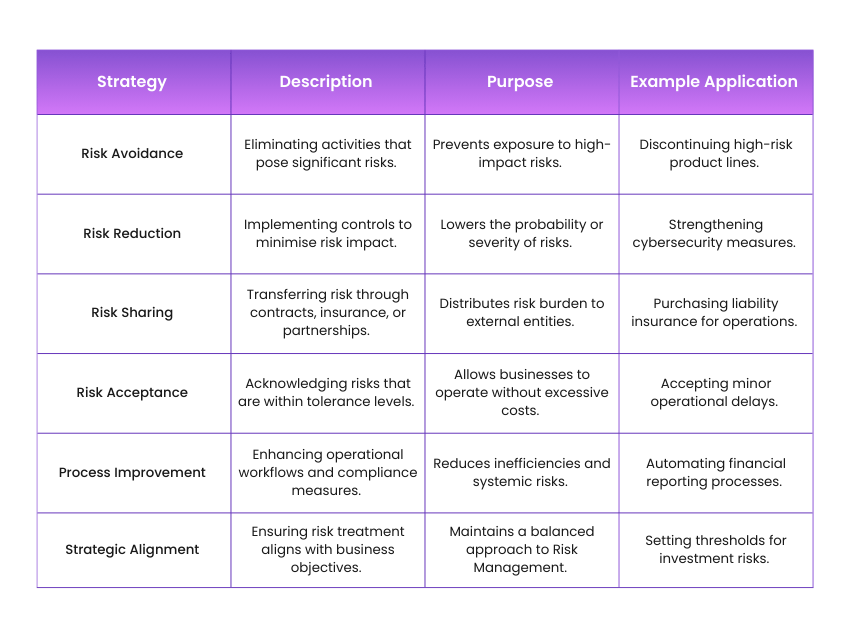
Step 4: Risk Treatment
1) Develop strategies to mitigate or eliminate identified risks
2) Implement risk avoidance by altering business activities
3) Reduce risk exposure through improved processes and controls
4) Share risks via insurance or partnerships
5) Accept certain risks when mitigation is not cost-effective
6) Align treatment strategies with organisational risk appetite
Step 5: Risk Monitoring
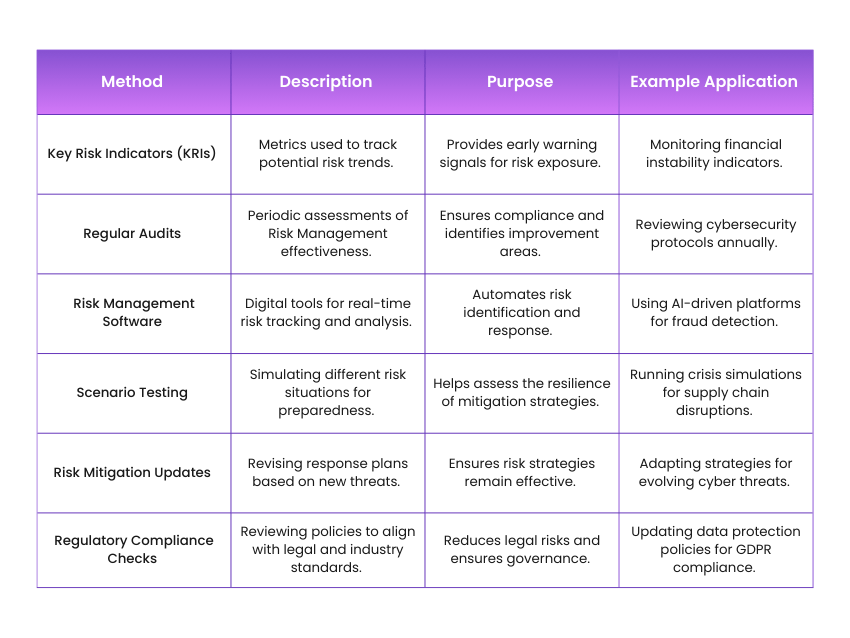
1) Continuously track and review risk exposure
2) Use Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) to measure risk trends
3) Conduct regular audits to assess Risk Management effectiveness
4) Implement Risk Management software for real-time tracking
5) Update mitigation strategies based on emerging risks
6) Ensure alignment with changing business conditions and regulations
How to Develop a Risk Management Plan?
A strong Risk Management Plan is the backbone of any successful project. It helps you spot possible problems early, plan how to handle them, and keep your project running smoothly. Let’s check how to develop such a plan:
1) Set Clear Objectives and Project Scope
Start by clearly defining your project’s goals and scope. This sets the direction for your team and helps everyone understand what success looks like. When the goals are clear, it becomes easier to see which risks could affect them.
1) Align goals with business priorities
2) Set clear, measurable targets
3) Involve stakeholders early to spot risks
Example: For our mobile app, the goal is to launch in six months, stay within budget, and deliver a user-friendly product. The scope covers design, development, testing, and a small marketing rollout to keep the team focused on key priorities.
Become a certified Project Management expert with our PRINCE2 Foundation & Practitioner Training - Register today!
2) Identify Risks in the Planning Stage
Once the goals and scope are set, you need to identify the possible risks. Think about anything that could delay progress, increase costs, or lower quality. Involve your whole team since they can help spot risks you might not have noticed.
1) Technical Problems: Bugs or crashes that delay the launch
2) Financial Issues: Extra costs for testing or design changes
3) Staff Shortages: Losing key team members or juggling too many projects
Example: During the mobile app project, the team identifies potential risks such as software bugs delaying the launch, budget overruns from unexpected design changes, and staff shortages affecting development timelines.
3) Assign Clear Roles and Responsibilities
Every good risk plan needs clear ownership. You need to decide who will track potential risks, update the plan, and take action when issues arise. This avoids confusion among everyone and keeps the process running smoothly.
1) Project Manager: Oversees the risk plan and updates the risk list
2) Lead Developer: Handles technical risks like bugs and performance issues
3) Financial Analyst: Keeps an eye on spending and financial risks
Example: In the mobile app project, the Project Manager oversees the entire risk plan, the Lead Developer handles technical issues, and the Financial Analyst monitors spending to manage budget-related risks.
4) Review and Update the Risk Management Plan
Once you know the risks and who is responsible, refine your plan. Decide how you’ll handle each risk, like whether to avoid it, reduce it, share it, or accept it. Keep reviewing the plan regularly so it stays up to date as your project changes.
1) Avoid risks by removing complicated features that could cause delays
2) Reduce risks by adding extra testing rounds to find bugs early
3) Share risks by outsourcing specific parts of development to experts
Example: Now, the team refines the plan by removing complex features that could delay launching, adding extra testing rounds to reduce bugs, and outsourcing certain tasks to manage workload and timelines.
5) Use Templates for Risk Management Plan
Using a template can save time and help you stay organised. Templates usually include sections for each risk, its impact, and the person responsible for managing it. They also make it easier to update and track risks as your project progresses, ensuring nothing important is overlooked.
1) Provides a uniform format for documenting and reviewing risks
2) Speeds up planning with ready-made sections for key details
3) Makes it easy to see each risk’s status and owner at a glance
Example: Here, the team uses a detailed template with columns for risk description, likelihood (low, medium, high), impact level, mitigation strategy, and assigned owner. This helps them record risk clearly and ensure accountability for every action taken.
Risk Management Frameworks
Several frameworks have been developed to guide organisations in managing risks effectively. These include:

1) ISO 31000: Risk Management Standard
ISO 31000 is an internationally recognised standard that provides principles and guidelines for effective Risk Management across various industries. It helps organisations systematically identify, assess, and mitigate risks, ensuring resilience and informed decision-making. This framework applies to businesses of all sizes, supporting them in achieving strategic objectives while managing uncertainties.
1) Comprehensive Framework: Establishes a structured approach to Risk Management.
2) Industry Agnostic: Applicable to organisations across various sectors.
3) Decision-Making Support: Enhances informed risk-based decision-making.
4) Regulatory Compliance: Helps align with legal and industry requirements.
5) Proactive Risk Mitigation: Encourages early identification and treatment of risks.
6) Continuous Improvement: Promotes ongoing evaluation and enhancement of risk strategies.
Align with business objectives while maintaining control over risks with our PRINCE2® Practitioner Training – Join now!
2) COSO ERM Framework: Enterprise Risk Management Approach
The COSO ERM Framework is a widely used model integrating Risk Management with corporate governance and strategic decision-making. It provides organisations a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and managing risks while aligning with business objectives. This framework enhances organisational resilience and fosters a risk-aware culture.
1) Enterprise-Wide Focus: Addresses risks across all levels of the organisation.
2) Governance Integration: Aligns Risk Management with corporate governance principles.
3) Strategic Risk Management: Supports informed decision-making at the executive level.
4) Risk Identification & Assessment: Provides a structured method for evaluating risks.
5) Performance & Resilience: Enhances business continuity and long-term success.
6) Compliance & Transparency: Helps organisations meet regulatory and ethical standards.
3) NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF): Cybersecurity Risk Management
The NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF) is a structured approach designed to help organisations manage cybersecurity risks effectively. It provides guidelines for integrating security, privacy, and Risk Management into organisational processes. This framework ensures compliance with regulatory standards while enhancing cyber resilience.
1) Cybersecurity Focus: Specialises in managing digital and information security risks.
2) Structured Process: Follows a step-by-step approach for risk assessment and mitigation.
3) Regulatory Compliance: Aligns with government and industry security standards.
4) Continuous Monitoring: Ensures ongoing risk evaluation and security updates.
5) Integration With IT Systems: Embeds Risk Management into system development and operations.
6) Enhancing Organisational Resilience: Strengthens defences against cyber threats and attacks.
4) Basel III: Risk Resilience for Financial Institutions
Basel III is a global regulatory framework designed to enhance Risk Management, financial stability, and regulatory compliance in the banking sector. It strengthens capital requirements, improves liquidity standards, and reduces systemic risks in financial institutions. This framework ensures banks can withstand economic downturns and financial crises effectively.
1) Stronger Capital Requirements: Mandates higher capital reserves to absorb losses
2) Enhanced Liquidity Standards: Ensures banks maintain adequate liquidity buffers.
3) Risk-Based Supervision: Encourages proactive identification and management of financial risks.
4) Leverage Ratio Regulation: Limits excessive borrowing to prevent financial instability.
5) Systemic Risk Reduction: Aims to protect the global financial system from economic shocks.
6) Regulatory Compliance: Aligns banks with international financial regulations and best practices.
Examples of Risk Management Strategies
Every business faces different kinds of risks depending on its industry, size, and goals. To handle these risks effectively, it is important to use a mix of strategies that suit your organisation’s needs. Here are some of the strategies:
1) Adopt Existing Frameworks and Best Practices
You don’t have to start from scratch when managing risks. There are well-known standards and frameworks that offer step-by-step guidance for identifying and handling risks. These can be adapted to fit your company’s goals and processes. Popular frameworks include:
1) ISO 31000: Offers clear principles and a structured approach to managing risks
2) NIST RMF: Focuses on cybersecurity and data protection
3) COSO ERM: Helps integrate Risk Management into everyday business decisions
2) Minimum Viable Product (MVP) Development
An MVP focuses on creating only the most important features of a product first. This allows you to test ideas, get feedback, and make improvements before investing more time and money. It helps reduce both financial and project risks.
1) Test your product with real users to gather early feedback
2) Use insights to fix problems before scaling up
3) Save time and money by avoiding unnecessary or unproven features
3) Develop Strong Contingency Planning
A contingency plan outlines what to do if things don’t go as expected. It prepares your team for emergencies or disruptions so you can respond quickly and limit damage. Having a clear backup plan also helps maintain confidence and stability during unexpected challenges.
1) Identify critical risks that could disrupt operations
2) Create step-by-step action plans for each scenario
3) Assign roles so everyone knows their responsibilities in a crisis
Adapt Agile practices within the structured environment of PRINCE2 with our PRINCE2 Agile® Practitioner Training – Sign up soon!
4) Root Cause Analysis and Lessons Learned
When something goes wrong, it’s important to understand why it happened. Root cause analysis helps identify the main reason for a problem and prevents it from happening again. Learning from past issues improves your future Risk Management.
1. Document lessons and share them with the wider team
2. Turn mistakes into learning opportunities to improve future projects
3. Use findings to refine risk policies and communication processes
5) Include Built-in Buffers
Adding a little extra time, money, or resources to your plan helps you stay flexible when unexpected issues arise. Buffers make it easier to handle changes without missing deadlines or going over budget.
1) Set aside a small portion of the budget for emergencies
2) Keep backup resources, such as extra staff or tools, ready if needed
3) Adjust buffer levels based on project complexity and risk
6) Perform a Risk-Reward Analysis
Before making a big decision, it is important to weigh the potential benefits against possible risks. This helps businesses make smarter, more balanced choices. Doing so ensures that resources are invested wisely and that downsides are understood before taking action.
1) Use data, research, and past results to guide your analysis
2) Focus on opportunities where rewards clearly outweigh risks
3) Review results regularly to update your understanding of acceptable risk
7) Conduct Third-party Risk Assessments
Getting an external expert to review your Risk Management Process can provide a fresh perspective and uncover issues you might have missed. This is especially helpful for new teams or companies looking to improve their approach.
1) Hire experienced consultants to review your risk processes
2) Ask for detailed reports with clear findings and recommendations
3) Use external feedback to strengthen internal risk controls
Risk Management Challenges
Despite the benefits of Risk Management, several challenges may arise, including:
1) Identifying Emerging Risks
1) Unforeseen threats such as technological disruptions and global crises
2) Rapidly evolving cyber threats increase vulnerability
3) Difficulty in predicting regulatory changes and compliance risks
4) Lack of historical data for assessing new and unprecedented risks
2) Inadequate Risk Awareness & Culture
Resistance to Risk Management adoption across departments
1) Lack of training and awareness among employees
2) Poor communication between Risk Management and decision-makers
3) Failure to integrate risk considerations into daily business operations
4) Resistance to Risk Management adoption across departments
3) Limited Risk Data & Analytics
1) Insufficient real-time data for proactive decision-making
2) Lack of standardised frameworks for risk assessment
3) Challenges in integrating multiple data sources for risk insights
4) Dependency on outdated or manual risk reporting methods
4) Regulatory Compliance Complexities
1) Frequent changes in local and global regulatory requirements
2) High costs associated with compliance and legal risks
3) Difficulty in aligning business operations with multiple regulations
4) Potential penalties and reputational damage from non-compliance
5) Resource Constraints in Risk Management
1) Limited financial investment in risk mitigation initiatives
2) Shortage of skilled professionals in risk analysis and management
3) Difficulty in securing executive buy-in for Risk Management strategies
4) Insufficient technological tools for effective risk monitoring
6) Challenges in Risk Monitoring & Response
1) Inability to continuously track and update risk mitigation efforts
2) Slow response to emerging threats and market fluctuations
3) Difficulty in aligning risk responses with business objectives
4) Over-reliance on reactive rather than proactive Risk Management strategies
Conclusion
Effective Risk Management isn’t about avoiding every challenge. It is about being prepared to face them confidently. By creating a structured Risk Management Process and using strategies like contingency planning, MVP development, and root cause analysis, businesses can respond faster, make smarter choices, and reduce uncertainty. When done right, this doesn’t just safeguard your organisation; it strengthens it for long-term growth and success.
Begin your Project Management journey with our PRINCE2® Foundation Training – Explore today!
 Contact@prince2training.co.uk
Contact@prince2training.co.uk 01344203999
01344203999





 Back
Back







 Continue Browsing
Continue Browsing
