Table of Content


Delivering a project on time and within scope is about hard work as well as smart strategy. Project Managers need more than intuition; they need proven techniques that can calm the chaos of a project lifecycle. From mastering timelines to fostering collaboration, these Project Management Techniques are the fuel behind successful outcomes.
If you are ready to elevate your projects from good to exceptional, you've come to the right place. This blog explores 12 of the most powerful Project Management Techniques that guarantee precision and efficiency. So read on and plan your roadmap to success!
What are Project Management Techniques?
Project Management Techniques refer to the frameworks and approaches used to plan, guide and control a project from start to completion. These techniques range from structured, linear models such as Waterfall to adaptive, iterative approaches like Agile.
While they differ in execution, they share the same objective: delivering successful outcomes through effective Risk Management, efficient use of resources, quality control, and timely delivery. Mastery of these approaches can set you apart as a strategic, adaptable professional capable of driving projects to success.
List of Common Project Management Techniques
Below are several Project Management Techniques commonly used across industries today. Gaining a clear understanding of these approaches can strengthen your skill set, improve your professional profile, and give you a competitive advantage when pursuing new career opportunities.
1) Waterfall Model
This is a traditional Project Management approach. It follows a sequential structure where each phase must be completed before the next begins. It is most effective when requirements are clearly defined from the outset and unlikely to change. This model benefits from detailed documentation and clearly defined milestones, making progress easy to track.
However, its rigid nature limits flexibility, making revisions difficult once a phase is completed. As it does not support ongoing feedback or iteration, the waterfall model is best suited to projects with fixed scope and timelines, such as construction or manufacturing.
2) Agile Methodology
This is an iterative Project Management approach designed for fast-changing environments where requirements frequently evolve. Rather than defining the entire project upfront, Agile promotes continuous feedback and regular adjustments throughout the project lifecycle.
Agile emphasises collaboration and team empowerment, enabling faster decision-making and greater responsiveness. However, it can be more challenging to manage in large, complex projects that demand strict schedules, fixed budgets and high levels of control.
3) Critical Path Method (CPM)
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a core Project Management technique for identifying the longest chain of dependent tasks that determines a project’s minimum completion time. This sequence, called the critical path, highlights activities that directly influence the overall schedule. It also highlights float for non-critical tasks. A delay to any task on the critical path will delay the entire project unless corrective action is taken. CPM typically involves:
a) Identifying all project activities
b) Defining their dependencies
c) Estimating task durations
d) Calculating earliest and the latest start and finish times
4) Six Sigma Technique
Six Sigma is a data-focused Project Management technique designed to minimise errors and improve process quality. It employs statistical analysis to identify root causes of defects and eliminate inefficiencies, helping organisations improve consistency, performance and profitability. This approach is widely applied in manufacturing and business operations.
5) PRINCE2® Methodology
PRINCE2® is a process-driven Project Management approach. It offers clear, step-by-step guidance, defined processes and well-established roles and responsibilities. It is widely used in the public sector and valued for its strong focus on quality control and Risk Management.
By dividing projects into manageable stages, PRINCE2® enables regular review and informed decision-making. Its structured framework also strengthens accountability and supports effective collaboration throughout the project lifecycle.
Manage projects and deliver excellence with our PRINCE2® Training – Register now!
6) Scrum
Scrum is an Agile-based Project Management technique designed for small, focused teams. It is led by a Scrum Master, who helps remove obstacles and ensures the team stays on track. Work is delivered in short cycles called sprints, typically lasting up to 30 days. Teams hold daily stand-up meetings to review progress and highlight challenges.
Scrum is commonly used for development and testing projects, such as UX initiatives, where priorities may change. This approach helps teams concentrate on high-value tasks and complete work in manageable stages.
7) Kanban
This is a visual Project Management approach that uses a Kanban board to display tasks, their current status and priority. The board is divided into columns such as pending, in progress, and completed, allowing teams to track work at a glance. Team members have shared access to the board.
As work progresses, tasks move between columns, highlighting progress, delays, and bottlenecks. As part of Agile Project Management, Kanban focuses on efficiency, continuous flow and clear visibility of current work.
8) Rational Unified Process (RUP)
Rational Unified Process (RUP) is a Project Management framework primarily used in software development. It supports the creation of early or beta versions of software, allowing teams to test functionality, evaluate performance and refine the product through multiple iterations. This iterative approach helps ensure a high-quality final release.
RUP encourages ongoing testing and adjustments as the project progresses, improving performance and user experience. It also allows early risk identification and strong quality assurance, ensuring the software meets required standards before launch.
9) Extreme Project Management
Extreme Project Management is designed for projects with high uncertainty, rapid change, and evolving requirements, where traditional planning methods are ineffective. It focuses on flexibility, continuous reprioritisation, and rapid decision-making to respond effectively to changing conditions.
By introducing structured daily, weekly or monthly routines, teams can complete recurring tasks better. For example, system updates or maintenance may be scheduled outside core working hours to minimise disruption and keep regular workflows running smoothly.
10) Project Network Diagrams
Project Network Diagrams are visual tools that illustrate a project’s activities and the relationships between them, showing how tasks are ordered and connected. They are commonly used alongside techniques like Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) and the Critical Path Method (CPM).
These diagrams use nodes to represent tasks and arrows to show dependencies, making it easier to understand workflow, identify critical paths and spot potential bottlenecks within the project schedule.
11) Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
The WBS is a Project Management technique used to divide a project into smaller elements that are more manageable. It provides a hierarchical breakdown of the total scope of work, offering a clear visual view of all tasks needed to complete the project.
Organised in a tree-like structure, these components are typically grouped into phases, deliverables, and tasks, becoming more detailed as the structure expands.
In Project Management, a WBS is used to:
a) Clearly define and structure the complete scope of a project
b) Ensure all required work is included while preventing scope creep
c) Provide a basis for estimating time, costs, and resources
d) Allocate tasks and responsibilities to team members
e) Support the creation of an accurate project schedule and budget
12) Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
PERT is a Project Management technique used when task durations are uncertain or subject to variation. Originally developed in the 1950s for the U.S. Navy’s Polaris missile programme, it helps Project Managers build schedules using probability-based time estimates. PERT involves creating a network diagram of project activities and assigning three time estimates to each task:
a) Optimistic Time (O): Shortest time the task could take.
b) Most Likely Time (M): Best estimate of how long the task will take based on available information.
c) Pessimistic Time (P): Longest time the task could take, considering all potential issues.
These values are combined to calculate the expected task duration using the formula:
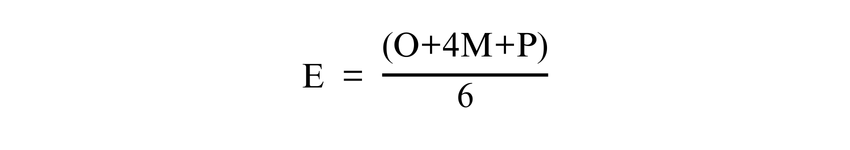
How to Choose the Right Project Management Technique?
Selecting the most suitable Project Management technique depends on the project’s size, complexity and overall nature. It is important to evaluate objectives, timelines, team capabilities and organisational culture before making a decision.
Projects that require frequent client feedback and evolving requirements are often well suited to Agile approaches. In contrast, projects with predictable outcomes and clearly defined phases that progress sequentially may benefit more from the Waterfall model.
Take the next big step in your Project Management journey with our PRINCE2® Practitioner Course – register now!
Benefits of Using Project Management Techniques
If you are unsure whether these techniques are necessary, explore the benefits they offer. Here are the key benefits:
1) Improved Team Collaboration
a) Defining tasks, owners, deliverables, and deadlines early prevents confusion and disorganisation.
b) Visual timelines or task lists help everyone understand who is responsible for what and when.
c) Project Management templates support repeatable processes and timely delivery of outputs.
d) Clear scope and scheduling make it easier to spot conflicts or risks before they escalate.
e) Structured planning reduces wasted time and effort across the team.
f) Breaking work into manageable sprints helps keep teams engaged throughout the project lifecycle.
2) Clear Roles and Accountability
a) Establishing a clear Project Owner prevents the tasks from being missed or details from being overlooked.
b) Defined ownership helps team members know exactly who to approach with questions or issues.
c) In the absence of a formal Project Manager, leadership responsibilities naturally fall to the project initiator.
d) Many roles already involve coordinating multiple moving parts alongside core responsibilities.
e) Effective Project Management does not require taking on an entirely new role.
f) Clear communication ensures everyone understands who is leading the project.
g) Outlining individual responsibilities removes uncertainty about team involvement.
3) Goal Focused Planning and Delivery
a) Clear project goals provide direction and purpose for the entire team.
b) Defined objectives prevent teams from focusing on low-impact or misaligned work.
c) Project Management tools help set and document goals at the outset.
d) Shared goals ensure everyone works towards the same outcomes.
e) Goals influence decisions and priorities throughout the project lifecycle.
f) Measurable objectives make it easier to evaluate project success.
g) A clear target or “north star” keeps teams focused on meaningful, high-impact tasks.
Start with the fundamentals of project success with our Introduction to Project Management Training - Sign up now!
4) Consistent and Effective Communication
a) Aligning on a communication plan before the work begins can improve clarity and coordination.
b) Clear guidelines define when to use email, messaging or project tools.
c) Consistent communication channels ensure that important information is not missed.
d) Reducing unnecessary tool switching helps teams stay focused.
e) A structured plan minimises confusion and information overload.
f ) Clear communication expectations keep everyone aligned and informed.
5) Higher Efficiency Through Structured Tools
a) Project Management tools help teams collaborate more fruitfully and stay organised.
b) They are especially ideal for complex projects where delays and cost overruns are common.
c) The right tools can support better tracking, coordination and progress visibility.
d) However, overly traditional tools can be time-consuming to set up and difficult to adopt.
e) Simple and customisable tools improve team adoption and efficiency.
f) Connecting work across projects reduces reliance on emails and spreadsheets.
Conclusion
Mastering the right Project Management Techniques is the key to empowering teams. These techniques help them turn ideas into results with greater clarity. By choosing the right approach for each project, you can manage risk, improve the collaboration process and deliver value consistently. Success comes from applying these techniques thoughtfully and keeping people and goals perfectly aligned.
From rigid plans to adaptive success, PRINCE2 Agile® transforms your approach. Sign up for our PRINCE2 Agile® Foundation and Practitioner Course now!
 Contact@prince2training.co.uk
Contact@prince2training.co.uk 01344203999
01344203999





 Back
Back







 Continue Browsing
Continue Browsing
