Table of Content

Every successful project begins with clarity and that clarity starts with a Project Initiation Document (PID). It's essentially the heartbeat that brings a project to life. Acting as a blueprint for direction, it transforms vague ideas into structured plans everyone can trust. Whether you are launching a small internal task or a large-scale strategic initiative, a well-crafted PID sets the stage for measurable success.
In this blog, we explore what a Project Initiation Document is, why it matters, and how to create one step by step to launch projects with confidence and control from concept to delivery successfully together. So read on!
What is a Project Initiation Document (PID)?
In Project Management, the Project Initiation Document (PID) is a comprehensive formal, document created during the initiation stage of a project. It brings together all the critical information needed to guide the project from its start through delivery.
It acts as the central reference for how the project will be planned, executed, monitored and controlled. The PID lays out the project’s direction, scope and management approaches so the team and stakeholders share a clear understanding of what will be done and how success will be measured.
Why is a Project Initiation Document Important?
The following contents within a Project Initiation Document illustrate why it's so important:
1) Client Information
The Project Initiation Documentation clearly records client details, stakeholder roles, and decision-making authority. This ensures accountability from the outset and avoids any confusion surrounding approvals, communication channels and expectations. This helps with maintaining strong alignment between the project team and the client throughout delivery.
2) Project Summary
The PID provides a concise overview of the project’s purpose, objectives, scope and justification. By documenting what the project aims to achieve and why it exists, it ensures everyone shares a common understanding of priorities and success criteria from the very beginning.
3) Task Summarisation
Task summarisation within the PID outlines the key activities, responsibilities and high-level timelines. This helps structure the work effectively by clarifying who is responsible for each area and supporting smoother coordination. This reduces the risk of missed tasks or overlapping responsibilities.
4) Project Metrics
Project metrics in the PID define how progress and performance will be measured. These include time, cost, quality and risk indicators, thus enabling informed decision-making, effective monitoring and early identification of issues that could impact successful project delivery.
Every stellar project starts with the right foundation. Begin yours with the Introduction to Project Management Course - Sign up now!
10 Components of a Project Initiation Document
Here are the 10 essential components of a Project Initiation Document that make it so vital to Project Management: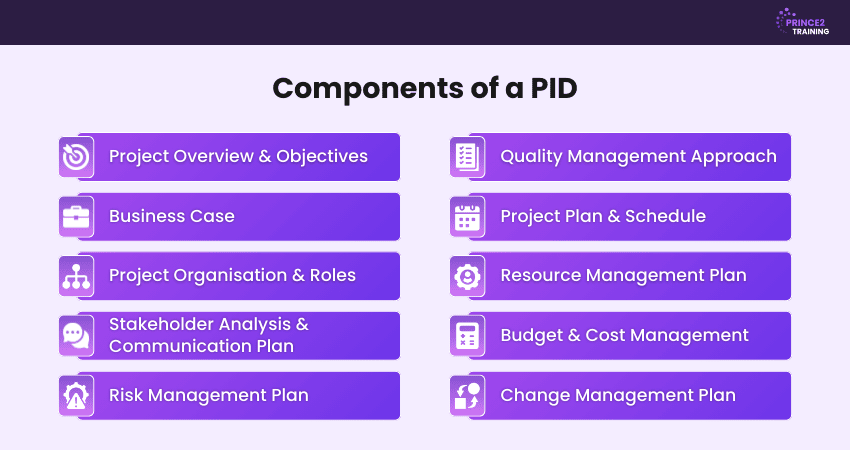
1) Project Overview and Objectives
This section explains the purpose of the project and clearly states what it intends to achieve. It provides a brief overview of goals, expected outcomes and organisational benefits, thus setting a clear direction from the start.
2) Business Case
The business case demonstrates why the project is worthwhile. It assesses the costs, benefits, risks and expected returns, which helps stakeholders evaluate value and overall feasibility before committing resources.
3) Project Organisation and Roles
Here, the project structure is defined, outlining roles, responsibilities and reporting lines. Clear allocation of authority supports effective communication, accountability and decision-making across the project team.
4) Stakeholder Analysis and Communication Plan
This component identifies the key stakeholders and analyses their interests and influence. It also defines how and when information will be shared, thus ensuring consistent engagement and transparency throughout the project lifecycle.
5) Risk Management Plan
This section documents the potential risks, their likelihood and impact, and the planned responses. Proactive Risk Management helps reduce uncertainty and allows the project team to address the issues before they affect delivery.
6) Quality Management Approach
Quality expectations and controls are set out here. It defines quality objectives, assurance methods and acceptance criteria, ensuring that outputs meet agreed standards and stakeholder expectations.
7) Project Plan and Schedule
The project plan outlines activities, milestones, dependencies and timelines. It provides a structured roadmap for delivery, thus enabling progress tracking and early identification of delays or constraints.
8) Resource Management Plan
This section details the resources required, including people, finances and materials. It explains how resources will be allocated and managed to support efficient and effective project execution.
9) Budget and Cost Management
Financial planning is covered in this component, which outlines the project budget, cost controls and contingency provisions. It ensures that the spending is monitored and kept within approved limits.
10) Change Management Plan
This section defines how changes to scope, requirements or objectives will be handled. A structured change process ensures that the impacts are assessed and approved, thus preventing uncontrolled changes from disrupting the project.
Combine the Agile mindset with the power of PRINCE2® to unlock assured project triumph. Sign up for the PRINCE2 Agile® Foundation Course now!
How to Create a Project Initiation Document?
Creating a Project Initiation Documentation is a structured process that helps set a project up for success. Below is a simple, step-by-step explanation of how a PID is created:
1) Project Initiation Meeting
The process starts with an initiation meeting where key stakeholders, the Project Manager and the team discuss the objectives, scope, limitations and expectations. This meeting creates a shared understanding and shapes the overall direction of the PID.
2) Gather and Analyse Project Information
The team collects essential details, including requirements, objectives and stakeholder expectations. They review existing documents, hold discussions and consult experts to gain a clear picture of the project. This information serves as the foundation for the PID.
3) Define Project Scope and Objectives
At this stage, the project scope is clearly defined, outlining what is included and excluded. The team defines clear and measurable objectives so everyone understands what success looks like and what the project aims to achieve.
4) Develop the Business Case
The business case explains why the project is needed. It looks at the costs, benefits, risks, and expected value. This shows how the project supports organisational goals and why it is worth undertaking.
5) Identify Stakeholders and Communication Plan
The team identifies all the stakeholders affected by the project and understands their needs and concerns. A communication plan is then crafted to define what information will be shared, how often and through which channels, thus ensuring consistent engagement.
6) Risk Management and Mitigation Strategies
The potential risks are identified and assessed based on their impact and likelihood. The team then plans actions to reduce or manage these risks. This helps prevent issues and ensures smoother project delivery.
7) Create Detailed Project Plan and Schedule
A detailed project plan is prepared, outlining tasks, milestones, deadlines and dependencies. Visual tools such as schedules or charts help the team track progress and make adjustments when required.
8) Resource Management and Budget Allocation
The resources including people, equipment and finances are allocated carefully. A clear budget is created to manage costs and contingencies, ensuring resources are used effectively and financial limits are respected.
9) Quality Management Approach
Quality standards and processes are defined to ensure deliverables meet agreed requirements. This includes setting quality checks and acceptance criteria to maintain consistency and stakeholder satisfaction.
10) Document Dependencies and Constraints
The team identifies key dependencies and constraints such as time, budget or regulatory requirements. Recording these helps manage expectations and plan work more realistically.
11) Review and Approval
Once completed, the PID is reviewed with stakeholders to gather feedback. After any updates, formal approval is obtained to confirm agreement and commitment to the project’s direction.
12) Regularly Update the PID
The PID is updated throughout the project to reflect changes in scope, risks, or resources. Keeping it current ensures decisions are based on accurate and up-to-date information.
Turn the toughest projects into the smoothest wins with PRINCE2® Practitioner Training - Register now!
Project Initiation Document Template
Here’s an ideal Project Initiation Document template:
Project Initiation Document (PID) – Template
1) Project Details
a) Project Name:
b) Project Sponsor:
c) Project Manager:
d) Project Start Date:
e) Expected Completion Date:
2) Project Overview: Offer a brief summary of the project, including its purpose and background. Explain what the project is about and why it has been initiated.
3) Project Objectives: List clear and measurable objectives that the project aims to achieve. These should define what success looks like.
4) Project Scope
a) In Scope: Describe what is included in the project.
b) Out of Scope: Clearly state what is excluded to avoid misunderstandings.
5) Business Case
Explain the justification for the project, covering:
a) Expected benefits
b) Estimated costs
c) Key risks
d) Strategic alignment
6) Project Organisation and Roles
Define roles and responsibilities:
a) Project Board
b) Project Manager
c) Team Members
d) Key Stakeholders
7) Stakeholder Analysis and Communication Plan
a) Identify key stakeholders
b) Outline their interests and influence
c) Define communication methods, frequency and responsibilities
8) Project Plan and Schedule
Provide a high-level plan including:
a) Key tasks
b) Milestones
c) Dependencies
d) Timelines
9) Resource Management
List required resources:
a) People
b) Tools or equipment
c) Budget allocations
d) Explain how resources will be managed.
10) Risk Management Plan
Identify major risks, including:
a) Risk description
b) Likelihood and impact
c) Mitigation actions
11) Quality Management Approach: Define quality standards, review methods, and acceptance criteria for deliverables.
12) Budget and Cost Management
Outline:
a) Approved budget
b) Cost control measures
c) Contingency planning
13) Change Management Plan: Describe how changes to scope, requirements, or timelines will be requested, reviewed, approved, and implemented.
14) Assumptions, Dependencies, and Constraints
a) Key assumptions
b) Internal and external dependencies
c) Constraints such as time, budget or regulations
15) Approval and Sign-off
a) Prepared by:
b) Reviewed by:
c) Approved by:
d) Approval Date:
Common Challenges in Developing a Project Initiation Document
Developing a Project Initiation Document without making it overly complex can be challenging. Below are some common challenges faced while creating and maintaining a PID:
1) Stakeholder Alignment
Keeping all stakeholders aligned is essential for project success. Any lack of agreement can cause confusion, delays, or disagreements once the project begins. Project Managers must ensure continuous alignment from the initial idea through to project completion.
2) Evolving Project Scope
Projects often evolve as work progresses. If clear boundaries are not defined early, the PID may become inaccurate. This can result in missed deliverables and schedule disruptions. Regularly reviewing and confirming the scope helps keep the project on track.
3) Improper Risk Identification
Failing to identify risks early is a common issue. Project Managers need input from different teams to recognise potential risks and plan responses. Poor risk identification can lead to unexpected issues later in the project lifecycle.
4) Poor Estimation
Estimating time, cost, and resources incorrectly can impact both schedules and budgets. Unrealistic estimates often lead to delays and added pressure during delivery, affecting overall project performance.
5) Documentation Overload
Highly collaborative projects can result in excessive or overly technical documentation. A PID should remain clear and accessible, thus ensuring both technical and non-technical stakeholders can easily understand and use it.
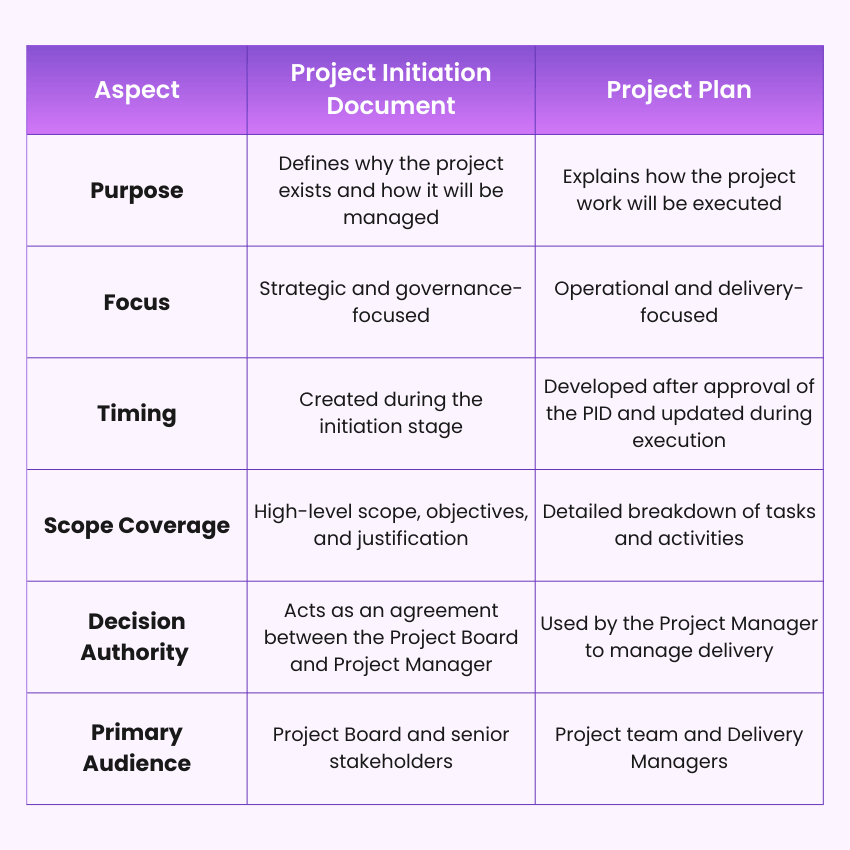
Project Initiation Document Vs Project Plan: Understanding the Differences
Here are the key differences between a Project Initiation Document and a Project Plan:
Conclusion
A Project Initiation Document transforms ideas into a solid structure. By defining the purpose, scope, risks and responsibilities early on, a PID can keep teams aligned and their decisions clear. When updated regularly, it becomes the backbone of successful delivery, helping projects move forward with focus and shared understanding from start to finish across teams and timelines.
Guide your projects to the finish line with ease. Sign up for a range of PRINCE2® Courses and achieve project excellence!
 Contact@prince2training.co.uk
Contact@prince2training.co.uk 01344203999
01344203999





 Back
Back







 Continue Browsing
Continue Browsing
