Table of Content

Success in business is shaped by more than internal plans and processes. Political decisions, economic shifts, social behaviour, and rapid technological change all influence how organisations grow. Ignoring these external forces can leave even strong strategies vulnerable. This is where PESTLE Analysis becomes essential, helping businesses spot risks and stay ahead of change before it happens.
By examining the wider environment, organisations gain clarity on what lies beyond their control and how to respond effectively. PESTLE Analysis supports smarter planning, sharper decision-making, and better alignment between business goals and external realities. In this blog, you will explore what PESTLE Analysis is, its key factors, how to carry it out, and why it matters for long-term success.
What is a PESTLE Analysis?
A PESTLE Analysis is a strategic planning framework used to examine external factors that influence an organisation’s performance and decision-making. It focuses on the key Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental (PESTLE) factors that shape the broader business environment.
By analysing these areas, organisations gain valuable insight into external risks, opportunities, and trends. This supports better strategic planning, informed decision-making, and the ability to adapt effectively to changing conditions.
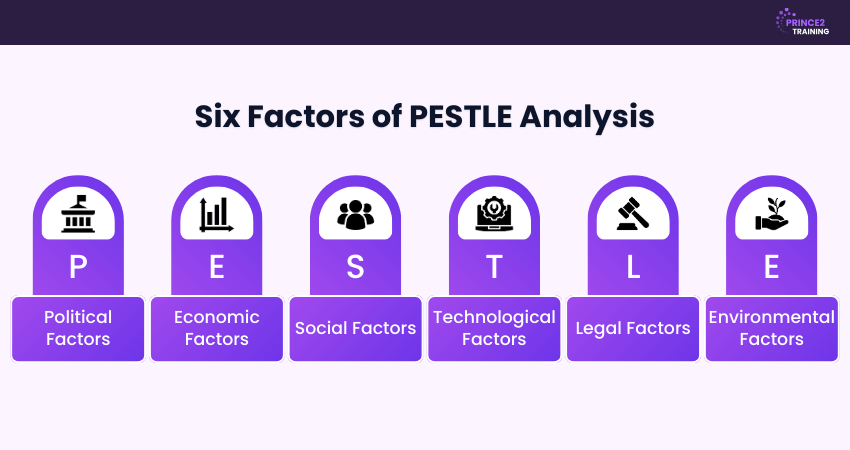
The 6 PESTLE Analysis Factors
PESTLE Analysis helps organisations understand external factors that influence their business performance and environment. It breaks these influential factors into six key categories to assess how current conditions can affect profitability, strategy, and long-term growth. Let's look at them in.
1) Political Factors in PESTLE Analysis
Political factors relate to government policies, political stability, and internal relations that can impact business operations. Changes in trade policies, government regulations, and political unrest can influence market entry, supply chains, and global expansion decisions.
Key Political Factors:
1) International Trade Agreements
2) Government Policies and Incentives
3) Political Stability or Unrest
4) Regulatory Changes
2) Economic Factors in PESTLE Analysis
Economic factors focus on the financial environment in which a business operates. These include economic growth, currency fluctuations, interest rates, and labour costs. These can affect consumer spending, investment decisions, and overall profitability.
Key Economic Factors:
1) Exchange Rates and Currency Strength
2) Inflation and Interest Rates
3) Labour Costs and Unemployment Levels
4) Economic Growth or Recession
3) Social Factors in PESTLE Analysis
Social factors examine changes in society, culture, and consumer behaviour that can shape customer preferences, brand perception, and market demand. Understanding these factors helps organisations align their products and marketing strategies with societal expectations.
Key Social Factors:
1) Demographics and Income Levels
2) Education and Lifestyle Trends
3) Cultural Norms and Values
4) Social Mobility and Consumer Attitudes
4) Technological Factors in PESTLE Analysis
Technological factors relate to innovations and advancements that can transform industries and business models. Emerging technologies can create opportunities for efficiency and growth, but they can also disrupt existing products and services.
Key Technological Factors:
1) Emerging Technologies and Innovation
2) Automation and Digital Transformation
3) Software and Hardware Developments
4) Consumer Technology Usage
5) Legal Factors in PESTLE Analysis
Legal factors include laws and regulations that affect how businesses operate. These rules can influence market entry, operational costs, compliance requirements, and competitive industry practices. Staying aware of legal changes is essential for ensuring compliance.
Key Legal Factors:
1) Employment and Labour Laws
2) Health and Safety Regulations
3) Data Protection and Privacy Laws
4) Competition and Advertising Laws
6) Environmental Factors in PESTLE Analysis
Environmental factors focus on ecological and sustainability issues that impact business operations. Climate conditions, environmental regulations, and sustainability expectations can influence production, location decisions, and corporate responsibility strategies.
Key Environmental Factors:
1) Climate and Natural Disasters
2) Sustainability and Environmental Policies
3) Waste Management and Emissions
4) Environmental Taxes and Incentives
Enhance your project management decision-making skills with the PRINCE2® Practitioner Course – Join now!
How to do a PESTLE Analysis?
PESTLE Analysis involves a structured process. By following a systematic approach, organisations can turn insights into actionable strategies and make informed decisions. Let's look at the steps below.
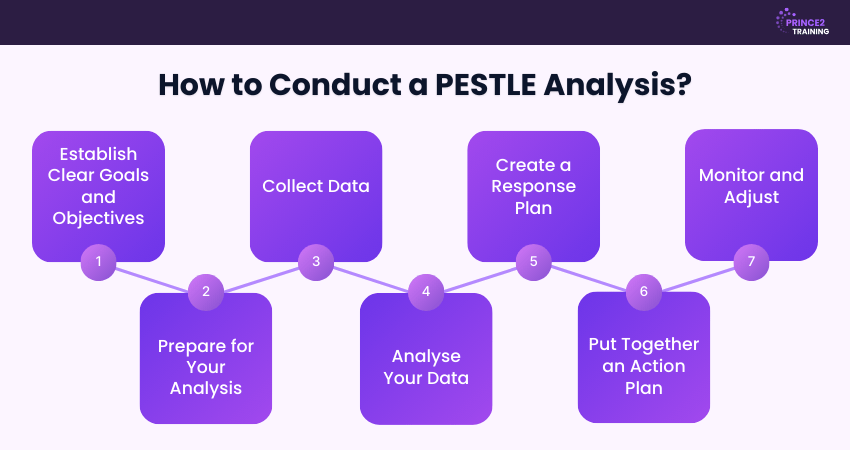
1) Establish Clear Goals and Objectives
Start by defining what you want to achieve from the PESTLE Analysis. Whether your goal is to identify opportunities, assess risk, or understand market trends, having clear objectives will guide the entire process smoothly. This step ensures your analysis stays focused and aligned with business priorities.
2) Prepare for Your Analysis
Preparation is essential for driving meaningful results. Here, involve relevant teams or stakeholders across the organisations to collect diverse perspectives. Plan meetings, design surveys, and decide how you will collect information to ensure structured input. Effective preparation improves collaboration and enhances the quality of insights.
3) Collect Data
Collect relevant information related to all six factors of the PESTLE Analysis. Utilise multiple sources, such as industry reports, case studies, market research, and internal data, to build a comprehensive understanding of the external environment. Accurate and reliable data form the foundation of a strong analysis.
4) Analyse Your Data
Evaluate the data to identify patterns, trends, opportunities, and threats. The key question at these implies what the findings mean for the organisation. By interpreting the data, you can understand how external factors impact performance and strategy. This step helps to transform raw information into meaningful strategic insights.
5) Create a Response Plan
Based on the analysis, develop a clear response plan. Identify actions needed to address risks or take advantage of opportunities. Break these actions into practical steps aligned with your organisational objectives. A well-defined response plan makes sure insights lead to practical business decisions.
6) Put Together an Action Plan
Transform your response plan into actionable tasks and integrate them into your business processes. Assign responsibilities, set timelines, and ensure accountability to turn strategy into execution. This step bridges the gap between planning and real-world implementation of the PESTLE Analysis.
7) Monitor and Adjust
External factors keep changing, so monitoring is essential. Review the effectiveness of your strategy regularly and adjust as needed. Flexibility ensures your organisation remains competitive and responsive to evolving market conditions. Continuous monitoring and reviewing help organisations stay proactive in dynamic environments.
Learn core principles and build a strong base in Project Management with PRINCE2® Foundation Course – Sign up now!
Advantages and Disadvantages of a PESTLE Analysis
PESTLE Analysis is a powerful strategic tool, but it also has certain limitations. Understanding both helps organisations use the framework effectively. Let's look at them below.
1) Advantages of a PESTLE Analysis
The advantages of PESTLE Analysis include:
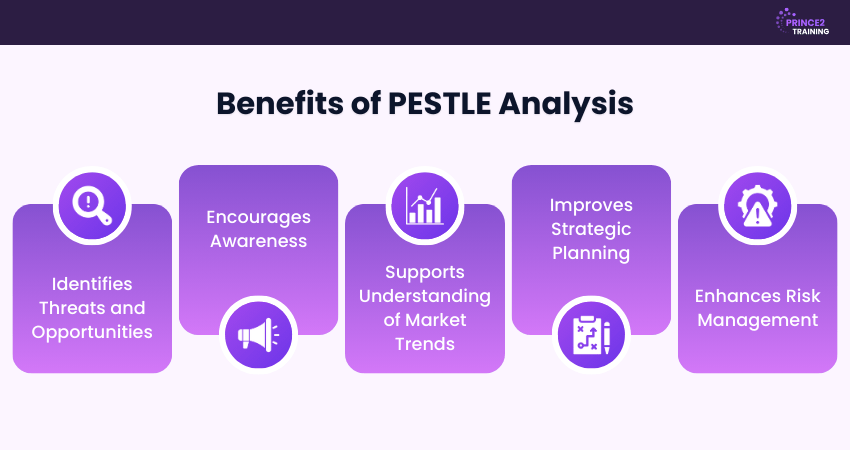
1) Identifies Threats and Opportunities: PESTLE Analysis helps organisations recognise potential risks and opportunities in advance, enabling proactive planning and better decisions.
2) Encourages Awareness: It pushes businesses to look beyond internal operations and consider political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental influences.
3) Supports Understanding of Market Trends: Analysing market trends helps organisations anticipate change in consumer behaviour, industry dynamics, and regulatory conditions.
4) Improves Strategic Planning: PESTLE Analysis provides a structured approach to decision-making, enabling organisations align strategies with external realities.
5) Enhances Risk Management: PESTLE Analysis helps businesses prepare for uncertainties by identifying external factors that may impact stability.
2) Disadvantages of a PESTLE Analysis
The disadvantages of PESTLE Analysis include:
1) Oversimplification of Complex Factors: This analysis may not fully capture the complexity of external influences affecting an organisation.
2) Subjective Interpretation: The result depends heavily on how the data is interpreted, which can lead to biased or inconsistent conclusions.
3) Time-consuming Process: Collecting and analysing external data can require significant time and resources, especially in dynamic industries
4) Rapidly Changing Environment: External factors evolve quickly, meaning the analysis may become outdated if not regularly updated.
Discover the fundamentals of successful Project with the Introduction to Project Management Course – Sign up today!
When Should You do a PESTLE Analysis?
PESTLE Analysis is valuable in situations where external factors can influence strategy and performance. It helps organisations anticipate change and make informed strategic decisions. Let's look at the situations when it is useful below.
1) Strategic Planning: PESTLE Analysis helps decision-makers understand the broader environment and identify opportunities and risks before developing long-term strategies.
2) Reviewing Market Positions: Organisations can use PESTLE Analysis to assess their market position, explaining the shifts in growth, decline, or stability. This helps businesses understand why their performance changes over time.
3) Marketing Planning: Marketing teams use PESTLE Analysis to understand external factors that influence campaigns, branding, and communication strategies. It helps marketers create messages that match current trends.
4) Product Development: PESTLE Analysis helps organisations understand consumer expectations and market trends from diverse perspectives, making it easier to design new products.
5) Organisational Change: When organisations undergo restructuring or expansion, PESTLE Analysis provides valuable insights into external factors that may impact the process. It reduces uncertainty and supports smoother transitions during strategic transformation.
Build hybrid Project Management for modern teams and deliver projects faster with PRINCE2 Agile® Foundation and Practitioner Course – Sign now!
Best Practices for PESTLE Analysis
For making PESTLE Analysis effective, organisations must go beyond listing external factors and focus on accuracy, relevance, and practical applications. Let’s look at some of the best practices below.
1) Get the Latest Data
Accessing the latest information is crucial for accurate analysis. Each PESTLE Analysis factor requires reliable data, such as economic indicators, political developments, or legal changes. Even small shifts in data can affect business decisions. So, organisations should always use the most recent information available.
2) Prioritise Facts Over Forecasts
While PESTLE Analysis involves future planning, it should be grounded in factual evidence. Organisations must avoid shaping data to fit assumptions or expectations, especially in dynamic areas, such as politics and economics. A fact-based approach ensures more realistic and reliable insights before making any business decision.
3) Get a Second Opinion
Getting input from multiple perspectives improves the quality of the PESTLE Analysis. Whether through external consultants, industry experts, or internal teams, a second opinion is useful for reducing bias and strengthening the accuracy of conclusions, especially for qualitative factors.
4) Incorporate Results in All Levels of Enterprise Planning
The results of a PESTLE Analysis should not be limited to strategic planning only. Organisations should make sure that insights are applied across every level of a business operation. From compliance and marketing to product development and implementation, this alignment helps to turn analysis into actionable strategies.
5) Use Visual Software for Presentation
Visual tools and software can make PESTLE Analysis interactive, engaging, and easier to understand. Using charts, templates, and collaborative platforms helps teams organise insights, communicate findings clearly, and share conclusions across departments.
Conclusion
Understanding external forces is essential for making smart business decisions in a constantly changing business world. Examining political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors helps organisations anticipate risks, identify opportunities, and build stronger strategies. When applied correctly, PESTLE Analysis becomes a powerful tool for informed planning, sustainable growth, and long-term success.
Learn proven methods to manage projects effectively and strengthen planning, control, and risk management with PRINCE2 Training – Sign up today!
 Contact@prince2training.co.uk
Contact@prince2training.co.uk 01344203999
01344203999





 Back
Back







 Continue Browsing
Continue Browsing
