Table of Content

Managing a project can feel like a race. The good news is that you can modulate your pace in this race in numerous ways and emerge a champion every time. Two methodologies that help you manage this pacing are Scrum and Kanban. Think of Kanban as the steady and adaptable runner, flowing effortlessly through each task, while Scrum is the sprinter, charging ahead in short, powerful bursts.
If you are struggling with the choice between the two, this blog’s got you covered. It explores the difference between Kanban vs Scrum, exploring how each method can reshape your workflow and keep your team on track for stellar results. So read on!
Table of Contents
1) What is Kanban?
2) What is Scrum?
3) Difference Between Kanban vs Scrum
4) Kanban or Scrum: Which is Right for You?
5) Advantages and Disadvantages of Kanban
6) Advantages and Disadvantages of Scrum
7) Conclusion
What is Kanban?
Kanban is a visual method for managing workflows that started with Toyota’s production system and is now popularly used in Software Development, Project Management, and other business areas. It uses a physical or digital board divided into stages and tasks are shown as cards that move across the board. This makes it easy for teams to track progress, spot delays, and boost efficiency.

Kanban can be understood through these key workflow stages:
1) Cadence: The pace of work is determined by the workflow stages set up on the Kanban board, such as ‘To Do’, ‘In Progress’, ‘Blocked’, and ‘Done’.
2) Release Method: Tasks are released when they are ready, without sticking to fixed schedules. If a task is completed early, it can be released immediately, and there’s no need for a sprint review.
3) Roles: Kanban boards are accessible to the whole team, but individuals can also have their own boards to manage specific tasks.
4) Metrics: Kanban uses metrics like lead time and cycle time to track progress. These metrics help identify how long tasks stay in each stage and reveal any bottlenecks in the workflow.
5) Change Philosophy: Kanban allows changes to happen at any time. Tasks can be added, removed, or blocked based on priorities.
What is Scrum?
Scrum is a Project Management method that organises work into short, focused periods called sprints. It involves breaking down projects into small tasks, known as user stories, to gather customer feedback at different stages and adjust plans accordingly.
Scrum can be broken down into the following components:
1) Cadence: Work is divided into two-week or month-long sprints, each with specific goals. Teams plan each sprint, hold daily stand-up meetings to stay on track, and review completed work for feedback.
2) Roles:
a) Scrum Master: Makes sure the team stays on track, manages processes, and maintains motivation.
b) Product Owner: Manages the product backlog, sets priorities, and defines project requirements.
c) Development Team: Completes tasks assigned within each sprint.
3) Metrics: Teams track data such as task completion time to assess progress and plan future sprints. Regular updates during stand-up meetings help Scrum Masters and Product Owners monitor and improve workflow efficiency.
4) Change Philosophy: Adjustments can only be made after a sprint ends. Unfinished tasks are reviewed, reassessed, and either carried over to the next sprint or moved back to the backlog. The retrospective meeting helps identify changes and improvements for the upcoming sprint.
Lead Agile projects successfully – Join the Scrum Master Certification today!
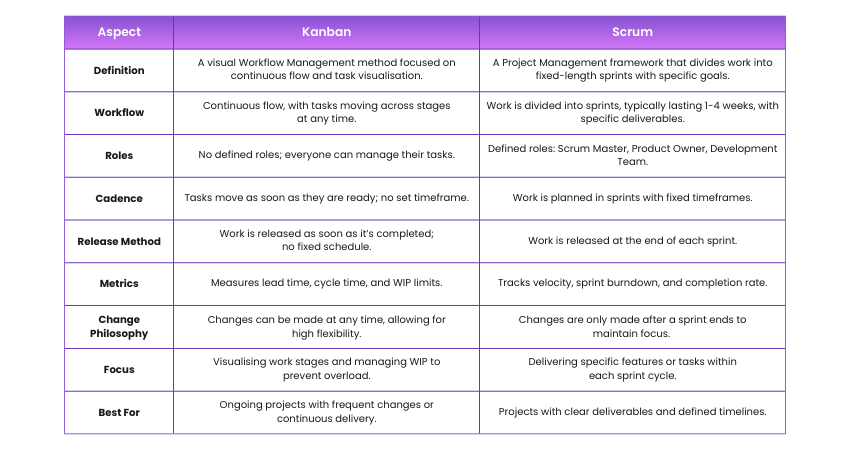
Difference Between Kanban vs Scrum
Here’s a summary of the key differences between Scrum and Kanban:
Kanban or Scrum: Which is Right for You?
Scrum and Kanban each offer distinct advantages, but it’s not necessary that you’ll have to choose one over the other. You can use both to get the best of both methods. Consider the following points:
1) When to use Kanban: Kanban helps you improve workflow visibility and promotes ongoing improvement, which eventually boosts productivity. It easily fits into existing processes, making it a great choice if you want to adopt Agile practices without completely changing your workflow.
2) When to use Scrum: Scrum is known for increasing productivity, speeding up delivery, reducing costs, and improving quality. It’s best for projects that require frequent changes or regular feedback, such as tech updates or new product development.
3) Scrumban: Scrumban takes a ‘best-of-best-worlds' philosophy by blending Scrum’s structure with Kanban’s visual tools. It’s a practical option for teams familiar with either method who want to incorporate elements of the other for better Workflow Management.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Kanban
Here are the pros and cons of Kanban to consider:
1) Pros:
a) Kanban boards provide a clear visual of work progress, keeping everyone aligned.
b) When a column gets crowded, it signals a mismatch between resources and demand.
c) It offers flexibility in setting priorities and making decisions at any stage.
d) Work queues can be adjusted based on new information without disrupting the overall workflow.
2) Cons:
a) Kanban boards don’t include deadlines, so it’s hard to predict how long a task will stay in each column.
b) If the board isn’t regularly updated, it won’t reflect the current project status accurately.
Juggle the chaos of project tasks with the cadence of project success with finesse! Sign up for our Agile Project Management Foundation (Agile PM®) Course now!
Advantages and Disadvantages of Scrum
Here are the pros and cons of Scum:
1) Pros:
a) Scrum has well-defined processes, roles, and timelines, making it easy to follow.
b) Short sprints allow teams to release work quickly, get feedback, and adjust for the next sprint.
c) Daily standup meetings help address issues promptly and keep everyone in sync.
2) Cons:
a) Scrum is strict about roles and processes, leaving little room for flexibility.
b) The constant sprint cycles can be demanding and leave little time for breaks or adjustments.
Conclusion
Kanban and Scrum may share the common goal of improving workflow, but they differ in their approaches. Kanban’s continuous flow suits ongoing projects, while Scrum’s structured sprints drive short-term goals. Making the right choice between Kanban vs Scrum depends on team dynamics, project needs, and the desired flexibility. Making the right decision is crucial for effective Project Management and successful outcomes.
Harness the power of Scrum and guide the agile ship with confidence! Sign up for our Scrum Master Training now!
 Contact@prince2training.co.uk
Contact@prince2training.co.uk 01344203999
01344203999





 Back
Back







 Continue Browsing
Continue Browsing
