Table of Content


Imagine trying to bake a cake before buying the ingredients, it wouldn’t make sense, right? The same goes for managing a project. Some tasks just can’t begin until others are complete, and this is where dependencies come in. They’re the invisible threads that link activities together, forming a logical sequence that keeps your project moving forward.
In this blog, we’ll explore what Dependencies in Project Management really mean, the different types you should watch for, and the real benefits of tracking them correctly. Whether you’re managing a small team or a large-scale rollout, mastering these is the secret ingredient to on-time, on-budget success.
Table of Contents
1) What are Dependencies in Project Management?
2) Types of Dependencies in Project Management
3) Types of Task Dependencies
4) How to Manage Dependencies in Project Management?
5) Benefits of Effective Dependency Management
6) Tools to Manage Project Dependencies
7) Practical Tips for Dependency Management
8) What is the Difference Between External and Internal Dependencies?
9) Conclusion
What are Dependencies in Project Management?
In Project Management, dependencies refer to the relationships between tasks or activities where one task relies on the start or completion of another. These links determine the order in which tasks must be performed and play a crucial role in scheduling, resource planning, and workflow coordination.
For example, you cannot begin painting a wall (Task B) until the wall is built (Task A). In this case, Task B is dependent on Task A.
Why Dependencies Matter:
1) They help define the logical sequence of work.
2) Prevent overlapping tasks that could cause delays or errors.
3) Allow Project Managers to identify critical paths and potential bottlenecks.
4) Improve time estimates and resource allocation.
Types of Dependencies in Project Management
Here are four types of Dependencies in Project Management.

1) Logical Dependencies
Logical Dependencies, also known as mandatory or hard logic dependencies, these are task relationships that are legally, contractually, or physically required. They are non-negotiable and must be followed for the project to progress.
Examples:
You must obtain building regulations approval before starting a construction project.
Legal contracts must be signed with the equipment supplier before purchasing factory machinery.
2) Preferential Dependencies
Preferential dependencies, or soft logic dependencies, are based on best practices, team experience, or preferred sequencing rather than strict necessity. They help optimise the workflow but can be adjusted if needed.
Examples:
Conducting quality checks after each development sprint in a software project, even though it could be done at the end.
Creating a draft presentation before finalising the data analysis, simply to give stakeholders an early view.
3) Cross-team Dependencies
These occur when the progress of one task or deliverable depends on the output of a different team. They are common in large, multi-department or cross-functional projects and require effective coordination.
Examples:
The design team must complete the user interface mock-ups before the development team can start coding.
The marketing team depends on product specifications from the engineering team to prepare a campaign.
4) Resource-based Dependencies
These dependencies arise due to limited availability of shared resources, such as equipment, personnel, or tools. Even if tasks are logically independent, they may need to be staggered due to resource constraints.
Examples:
Only one video editor is available, so editing can’t begin on the next video until the first is done.
A specialist consultant is needed for two tasks, so they must be scheduled one after the other.
5) External Dependencies
External dependencies are task relationships that rely on actions or deliverables outside of the project team’s direct control. These might involve third parties such as clients, suppliers, government agencies, or other external stakeholders.
Examples:
Waiting for government approval or permits before beginning construction.
Relying on a vendor to deliver software licences before installation can begin.
Dependent on a client to provide key data before analysis or planning work starts.
Take the next step in project leadership with PRINCE2 Foundation & Practitioner Course – Register today!
Types of Task Dependencies
Understanding task dependencies helps you schedule work in the correct order and avoid project delays. Here are the four main types you should know:

1) Finish-to-Start (FS)
This is the most common dependency. Task B cannot start until Task A finishes. You must complete development (Task A) before you can start testing (Task B).
2) Finish-to-Finish (FF)
Task B cannot finish until Task A finishes. Both tasks may run in parallel but must end together. Writing a report (Task A) and proofreading the report (Task B) can happen concurrently, but proofreading finishes only after writing is complete.
3) Start-to-Start (SS)
Task B cannot start until Task A starts. Both begin around the same time, but Task B depends on the initiation of Task A. Start pouring concrete (Task A) and begin smoothing the surface (Task B), smoothing starts only after pouring begins.
4) Start-to-Finish (SF)
Task B cannot finish until Task A starts. This is the least common dependency. A night shift worker (Task B) cannot finish their shift until the day shift worker arrives (Task A).
How to Manage Dependencies in Project Management?
Managing dependencies is essential for keeping your project timeline on track. By following a few key practices, you can reduce delays, improve coordination, and ensure smoother execution from start to finish. Here's how to do it effectively:
1) Identify and Document all Dependencies
The first step in managing dependencies is to recognise them early.
a) List all tasks and their related dependencies early in the planning stage
b) Categorise them (logical, resource-based, external).
c) Use a dependency log or project management tool for visibility
2) Define the Critical Path Clearly
The critical path is the longest sequence of dependent tasks that determines the project’s minimum duration
a) Map out the sequence of tasks that directly impacts the project deadline
b) Identify tasks with zero float (no room for delay)
c) Focus resources and monitoring on critical tasks
3) Keep Stakeholders Updated
Dependency management requires strong communication.
a) Communicate dependencies across teams and departments
b) Share updates regularly through reports, dashboards, or meetings
c) Ensure everyone understands how changes may affect others
4) Continuously Monitor Risks
Dependencies, especially external ones, can introduce risks such as delays, miscommunication, or lack of resources.
a) Review dependencies frequently to spot delays or issues early
b) Assess risk levels for each dependency
c) Prepare contingency plans (e.g. backup resources or buffer time)
Benefits of Effective Dependency Management
Effective Dependency Management is crucial for keeping projects on track. Here are some of the benefits of the same:
1) Improved Project Planning: Helps structure tasks logically, ensuring smoother project flow and realistic timelines.
2) Minimised Delays: Early identification of task relationships allows you to prevent bottlenecks and reduce schedule risks.
3) Better Resource Allocation: Enables you to assign the right resources at the right time, avoiding conflicts or overbooking.
4) Enhanced Team Coordination: Keeps all teams aligned by clarifying who depends on whom, improving collaboration and communication.
5) Stronger Risk Management: Allows proactive identification of high-risk dependencies, especially external or cross-functional ones.
6) Clearer Stakeholder Visibility: Keeps clients and team members informed about task progress and interdependencies.
7) Increased Project Success Rate: Leads to on-time delivery, better quality outcomes, and higher stakeholder satisfaction.
Take charge of projects the professional way – Join PRINCE2® Foundation Course now!
Tools to Manage Project Dependencies
Using the right tools makes it easier to track, visualise, and manage task relationships throughout your project. Here are some of the most effective ones:
1) Gantt Charts
Gantt charts are visual timelines that display project tasks and their durations. They show how tasks relate to each other, making it easy to identify and manage dependencies. Project managers can adjust dates and see how one change affects the rest of the timeline.

2) Kanban Boards
Kanban boards organise tasks into columns like “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done.” While they focus more on task status than sequence, dependencies can still be managed by linking cards or using labels to indicate waiting tasks or blockers.

3) Dashboards
Dashboards give a real-time overview of project progress, highlighting key dependencies, delays, and bottlenecks. They help teams monitor updates and stay aligned, especially when managing multiple tasks across teams.
4) Online Calendars
Online calendars help teams schedule tasks, meetings, and deadlines. By sharing timelines, teams can coordinate start and end dates, helping prevent conflicts and manage time-based dependencies more effectively.

Practical Tips for Dependency Management
Here are some actionable tips to help you stay in control of task relationships throughout your project lifecycle:
1) Use Project Management Software to Organise Tasks
Using the right project management tool makes it easier to structure tasks, assign responsibilities, and track dependencies efficiently.
a) Choose tools like Asana, ClickUp, or MS Project for better visibility
b) Break projects into smaller tasks with clear owners and deadlines
c) Link dependent tasks so delays automatically reflect across the timeline
d) Keep everything centralised to reduce miscommunication
2) Clearly Visualise Dependencies
Seeing how tasks connect helps teams stay aligned and avoid delays. Visual tools make it easier to spot bottlenecks early.
a) Use Gantt charts or Kanban boards to map dependencies
b) Colour-code tasks based on priority or type of dependency
c) Mark critical paths to highlight tasks that impact delivery
d) Update visuals regularly as the project evolves
Learn the method and lead with Introduction to Project Management Course – Register today!
3) Promote Stakeholder Collaboration
Dependencies often span teams, so consistent communication is key to avoiding misalignment and missed deadlines.
a) Keep stakeholders updated through dashboards or status meetings
b) Share dependency logs across teams to ensure visibility
c) Encourage early feedback to resolve cross-team issues
d) Assign a contact person for each major dependency
4) Monitor Risks Throughout the Project Plan
Dependencies can cause delays if left unmanaged. Proactively tracking them reduces surprises and keeps the project moving.
a) Review high-risk dependencies during each project review
b) Add buffer time for tasks reliant on external parties
c) Set reminders for upcoming dependencies or deadlines
d) Have a backup plan for critical resources or vendors
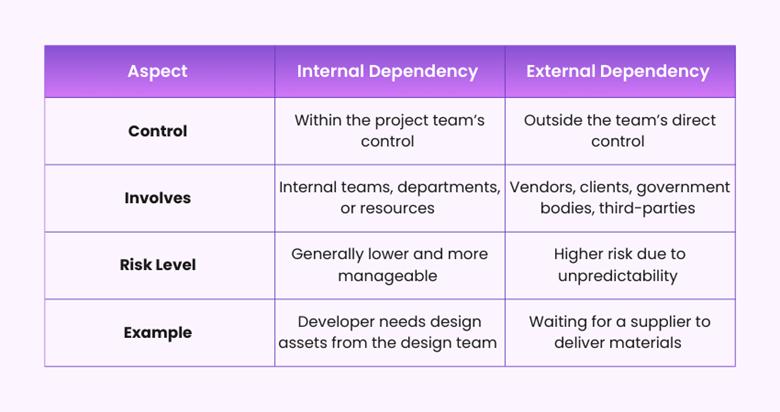
What is the Difference Between External and Internal Dependencies?
Internal dependencies occur within the project team or organisation, where one task or team relies on another internal task or resource to proceed. These are typically easier to manage because they are under the project manager’s control.
External dependencies, on the other hand, involve factors or parties outside the organisation. These may include clients, vendors, regulatory bodies, or third-party service providers, and are often more unpredictable due to limited control.
Conclusion
Dependencies in Project Management help define the order of tasks and ensure smooth project flow. By understanding their types and managing them effectively, teams can avoid delays, improve coordination, and boost overall success. Recognising and tracking dependencies is a key part of keeping projects on time, within scope, and running efficiently from start to finish.
Advance your project career with expert-level PRINCE2 Training – Sign up now!
 Contact@prince2training.co.uk
Contact@prince2training.co.uk 01344203999
01344203999





 Back
Back







 Continue Browsing
Continue Browsing
