Table of Content

A single interruption can costa business money, trust, and loyal customers. That’s why smart organisations prepare before problems arise. A Business Impact Analysis helps identify critical tasks, possible risks, and the best recovery steps, ensuring operations stay steady even during disruptions.
In this blog, we will explain Business Impact Analysis in simple terms. You will learn what it is, why it matters, key elements, how to conduct it, and how it differs from risk assessment, helping your organisation stay prepared and resilient.
What is Business Impact Analysis (BIA)?
Business Impact Analysis (BIA) is a process that identifies the critical activities of an organisation, evaluates the potential impact of disruptions, and determines the resources required to restore operations. It’s not just about preparing for disasters but about equipping your business to handle anything from IT failures to supply chain interruptionsx.
At its core, BIA answers essential questions:
1) Which operations are most critical to the organisation?
2) What would happen if those operations were disrupted?
3) How quickly can they be restored?
By understanding these factors, businesses can create effective recovery plans and ensure resilience in the face of adversity.
Why is a Business Impact Analysis Important?
You might be wondering, “Why bother with a BIA when we already have a risk management plan?” While risk management focuses on preventing threats, BIA is about preparing for the aftermath. Here’s why it’s a game-changer:
1) Prioritising Resources
During a crisis, you cannot focus on everything at once. A BIA helps you see which processes, projects and departments are most important. This allows you to use your time, people, and tools wisely, ensuring essential work continues first.
2) Minimising Downtime
When business stops, money and customers can be lost quickly. A BIA helps you understand how fast you need to get things running again. With clear recovery priorities, you can reduce downtime and keep operations moving as smoothly as possible.
3) Protecting Reputation
Customers trust businesses that respond quickly to problems. With a BIA, you can recover faster and continue serving customers without long delays. This protects your brand image and prevents frustration, helping you maintain strong customer loyalty and confidence.
4) Regulatory Compliance
Many industries, such as finance and healthcare, must follow rules related to emergency planning. A BIA helps you meet these rules and avoid penalties. It also shows regulators that your business is responsible and prepared for unexpected events.
5) Enhancing Decision-Making
A BIA gives leaders clear information about the effects of disruptions. With this insight, they can make better decisions during emergencies in their project. Instead of guessing, they can act confidently, protect the business, and choose the best steps to recover.
Boost your Software Testing skills with our ISTQB Advanced Level Technical Test Analyst Training - Register today!
Elements of Business Impact Analysis
Conducting an effective BIA involves a thorough evaluation of the key areas within your organisation. The following are its core elements:

1) Identifying Critical Business Functions
Identifying critical business functions means finding the most important tasks that keep your business running smoothly. These may include areas like sales, customer support, IT, and production. When you know your key functions, you can protect them better during a disruption.
2) Assessing Potential Risks
Think about all the problems that could interrupt your business. It could be anything from cyberattacks and equipment issues to health emergencies or supply delays. Understanding possible risks helps you plan ahead and avoid major losses.
3) Analysing Impact Scenarios
Here, you check how different problems would affect your business. For example, if your website goes down for a day, you might lose sales and frustrate customers. This step helps you understand the financial and service impact of disruptions.
4) Defining Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs)
RTOs set the maximum time you can allow a business function to be down before it causes serious harm. This helps you decide what to fix first when a problem arises. Clear recovery timelines keep your team focused and organised in emergencies.
5) Identifying Dependencies
RTOs set the maximum time you can allow a business function to be down before it causes serious harm. This helps you decide what to fix first when a problem arises. Clear recovery timelines keep your team focused and organised in emergencies.
6) Resource Allocation
Decide what resources are needed to recover from disruptions, such as backup tools, trained staff, or funds for emergencies. Planning resources ahead of time helps you act quickly during a crisis. It ensures you have everything ready when unexpected events happen.
How to Conduct a Business Impact Analysis?
Now that we’ve covered the “what” and “why,” let’s move on to the “how.” Conducting a BIA might sound daunting, but breaking it into manageable steps makes the process straightforward and effective.
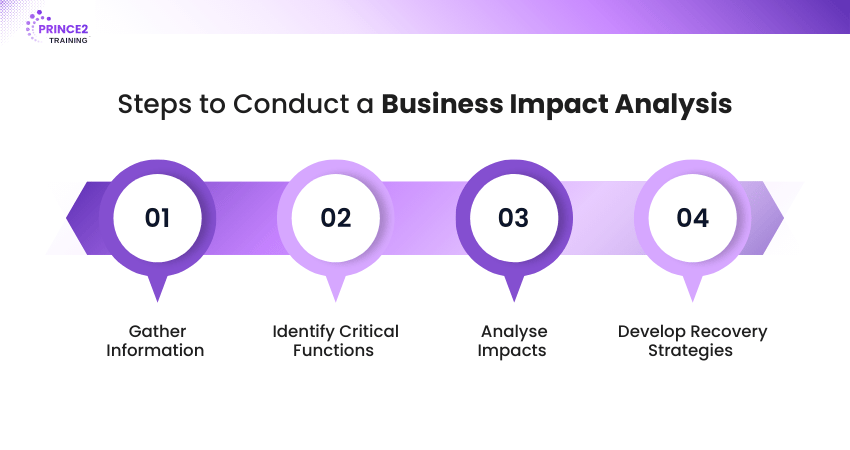
Step 1: Gather Information
Start by collecting data about your organisation’s processes, resources, and risks. This step typically involves:
1) Interviews and Surveys: Talk to department heads and key stakeholders to understand their roles and responsibilities.
2) Document Analysis: Review existing policies, workflows, and recovery plans.
3) Risk Assessment: Verify potential threats and their likelihood of occurrence.
The goal is to get a comprehensive picture of your organisation’s operations and vulnerabilities.
Step 2: Identify Critical Functions
Not all functions are created equal. Some are essential to keep the lights on, while others can wait during a crisis. Categorise your business functions into:
1) Mission-Critical: Functions that must be restored immediately (e.g., IT systems, customer service).
2) High Priority: Important but can be delayed slightly (e.g., marketing campaigns).
3) Non-Essential: Functions that can be paused without major consequences (e.g., routine maintenance).
This prioritisation ensures that your resources are allocated efficiently during disruptions.
Step 3: Analyse Impacts
Once you’ve identified critical functions, assess the potential impacts of disruptions:
1) Financial Impact: Calculate revenue loss, penalties, and additional costs.
2) Operational Impact: Determine how disruptions affect productivity and workflows.
3) Reputational Impact: Consider how delays or failures might harm your brand’s reputation.
This step provides a clear picture of what’s at stake, helping you plan accordingly.
Step 4: Develop Recovery Strategies
Finally, actionable strategies should be created to mitigate risks and recover quickly. These strategies might include:
1) Backup Plans: Establish alternative suppliers, systems, or workflows.
2) Emergency Funds: Set aside financial reserves to cover unexpected costs.
3) Training Programs: Equip employees with the skills needed to handle disruptions.
Document these strategies in a comprehensive BIA report and integrate them into your business continuity plan (BCP).
Business Impact Examples
A BIA helps a company see how disruptions affect key operations and what steps keep things running. Here is the Business Impact Analysis example:
Example 1: Retail Payment System Failure
Situation: The card payment machine stops working in a supermarket.
Impact:
a) Long queues
b) Customers leave without buying
c) Daily sales drop
d) Store reputation suffers
BIA Helps:
a) Plan backup like cash counters or mobile card devices
b) Train staff on manual billing
c) Ensure quick service recovery
Example 2: Factory Machine Breakdown
Situation: A key machine in a manufacturing plant breaks down.
Impact:
a) Production stops
b) Orders are delayed
c) Increased repair and labour costs
d)Customer trust may decrease
BIA Helps:
a) Keep spare parts and maintenance plans ready
b) Schedule regular equipment inspections
c) Set up alternate production arrangements
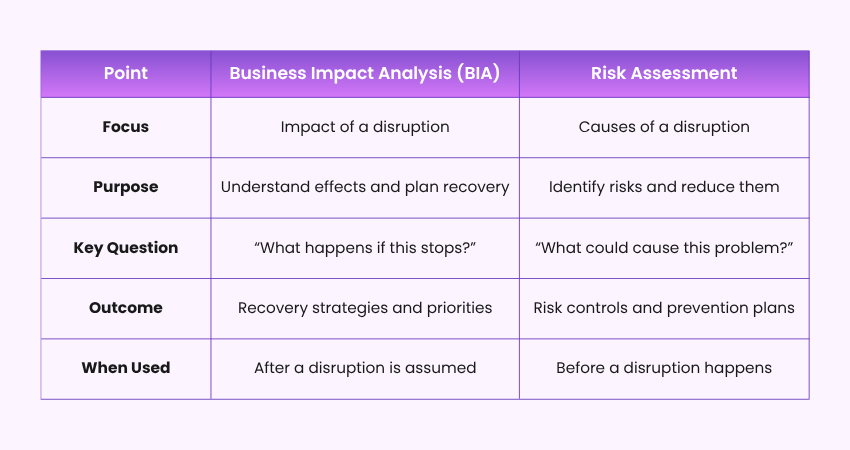
Business Impact Analysis vs Risk Assessment
A BIA focuses on what happens after a disruption. It shows how it affects work, money, and customers and helps plan how to recover quickly. A Risk Assessment focuses on what could cause a disruption. It finds possible risks and helps prevent them.
Conclusion
Preparing for disruption is essential in today’s fast-paced world. With the right planning and focus, businesses can stay strong even when challenges arise. A Business Impact Analysis helps protect key operations, reduce downtime, and support confident decision-making. By prioritising what matters most, you build a resilient organisation ready to keep moving forward in any situation.
Advance your career in Business Analysis with our BCS Certificate in Business Analysis Practice.. Join our next batch today!
 Contact@prince2training.co.uk
Contact@prince2training.co.uk 01344203999
01344203999





 Back
Back







 Continue Browsing
Continue Browsing
