Table of Content


Project Management is about guiding a vision from concept to completion while keeping time, budget and quality in perfect synergy. From a PR event and App launch to building a skyscraper, Project Management is the key to
ensuring everything goes smoothly.
This blog will serve as the ideal introduction to Project Management as it explores the types, phases and proven tips to achieve project excellence. So read on and give structure to your creativity and vision!
What is Project Management?
Project Management involves using specific processes, techniques, skills, knowledge, and experience to achieve defined project goals within agreed-upon timelines and budgets. It is goal-oriented, delivering a distinct output within a set timeframe.What sets Project Management apart from general management is its finite scope. While general management is continuous, Project Management has a clear endpoint marked by the successful delivery of the project. As such, Project Managers require a blend of technical expertise, strong People Management capabilities, and solid business insight to ensure success.
Why Is Project Management Important?
Project Management is essential for the thriving enactment of large-scale projects. Rather than concentrating solely on one outcome, Project Management breaks the project into smaller, more manageable tasks. These tasks are documented, evaluated, and monitored throughout the process.
This ensures they collectively contribute to achieving the greater objective. The qualities of Project Management lie in its capability to effectively guide projects to their intended outcomes, ensuring that end objectives are satisfied efficiently and on time.
Who Uses Project Management?
Project Management is not exclusive to those with the title of 'Project Manager'; it's a skill many people apply daily. Whether organising an event or coordinating a team effort, nearly everyone manages projects in some form. Beyond personal tasks, formal projects are integral to various industries, including:
1) Transport and Infrastructure
2) IT and Technology
3) Product Manufacturing
4) Building and Construction
5) Finance and Law

Types of Project Management
Now, let's look at the various types of Project Management. All these provide a different approach and prove efficient for different scenarios.
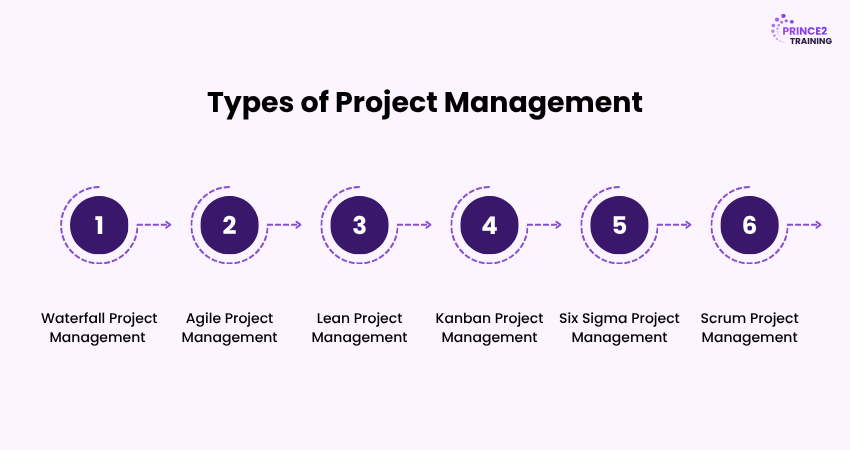
1) Waterfall Project Management
A traditional, linear approach where tasks are completed sequentially, requiring strict adherence to timelines and task order. As smaller tasks finish, larger ones begin, often increasing team size.
2) Agile Project Management
An iterative, non-linear process emphasising flexibility, continuous improvement, and customer value. Phases run parallel, allowing for rapid error correction and adaptation to changing business needs.
3) Lean Project Management
Focused on minimising scrap and maximising customer value, using only essential resources to achieve project goals, similar to lean enterprise principles.
4) Kanban Project Management
A visual workflow system using a Kanban board, where tasks move through columns representing progress. It enhances transparency, prioritisation, and productivity.
5) Six Sigma Project Management
A data-driven process improvement approach that minimises defects using the DMAIC framework (Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, Control), ensuring sustained results.
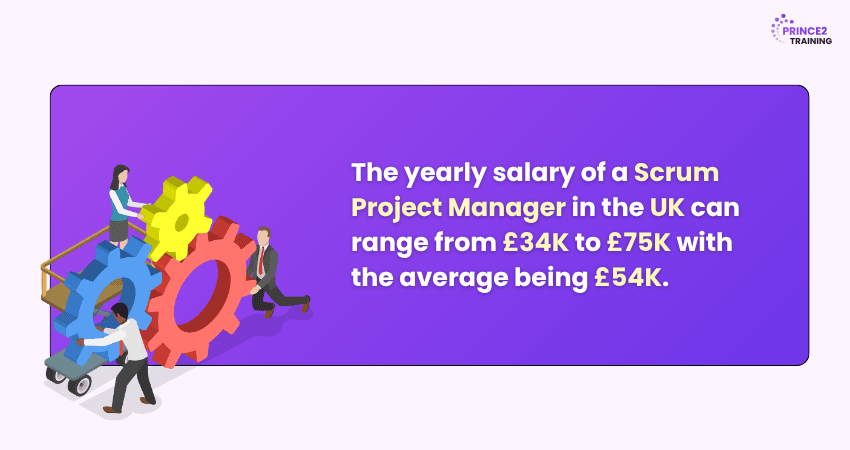
6) Scrum Project Management
An Agile framework that breaks projects into sprints (1-4 weeks). Teams collaborate daily, adapting quickly and delivering value incrementally. Each sprint ends with a review to gather feedback and refine processes.
Approaches of Project Management
There’s no single formula for managing projects effectively. The ideal approach depends on factors like project complexity, industry standards, organisational goals, team culture, and the level of flexibility required. Here are some of the most common project management approaches:
1) Predictive Project Management’
Predictive Project Management also called traditional or Waterfall, this is a structured approach where every phase is completed before moving on to the next. It suits those projects that have fixed goals and stable requirements. Methods like CPM and PRINCE2 fall under this category.
2) Adaptive Project Management
Also referred to as Agile, this flexible style breaks every work into short iterations or sprints. It encourages constant feedback and accommodates evolving project needs. It's ideal for product development. Common frameworks include Scrum, Kanban and Extreme Programming (XP).
3) Hybrid Project Management
This approach merges predictive structure with agile flexibility. Teams can plan strategically while staying adaptable. Scrumban, which blends Scrum and Kanban, is a popular hybrid example that offers both control and agility.
4) Project Portfolio Management (PPM)
When multiple projects are managed jointly under one strategic umbrella, it becomes a portfolio. Project Portfolio Management ensures projects are prioritised, aligned with business goals, and deliver maximum value. Strategic Portfolio Management goes a step further by aligning resources and investments directly with organisational vision and its long-term impact.
Become a certified Project Management Professional and elevate your career—join our Project Management Professional (PMP)® Training now!
What are the 10 Areas of Project Management?
Project Management is structured around ten key knowledge areas that guide the planning, execution, and control of projects in any industry. These areas help ensure projects run smoothly and achieve their goals effectively. Here are the ten core areas:
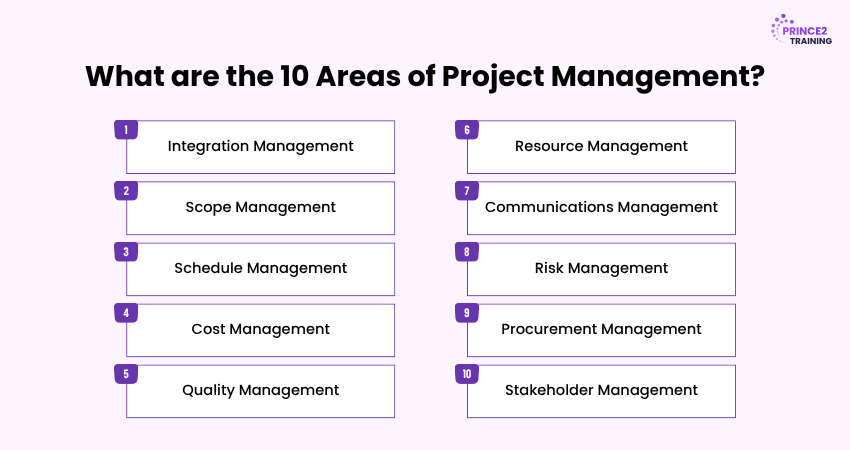
1) Integration Management: Ensures all project elements are aligned and work together.
2) Scope Management: Defines what the project will and won’t include.
3) Schedule Management: Plans and monitors timelines and deadlines.
4) Cost Management: Focuses on budgeting, estimating, and controlling expenses.
5) Quality Management: Makes sure outputs meet required standards.
6) Resource Management: Handles team coordination and allocation of resources.
7) Communications Management: Ensures clear and timely information flow.
8) Risk Management: Anticipates and addresses potential issues or uncertainties.
9) Procurement Management: Manages the sourcing of external services or materials.
10) Stakeholder Management: Engages and maintains positive relationships with stakeholders.
Five Phases of Project Management
Here are the five phases of project management:
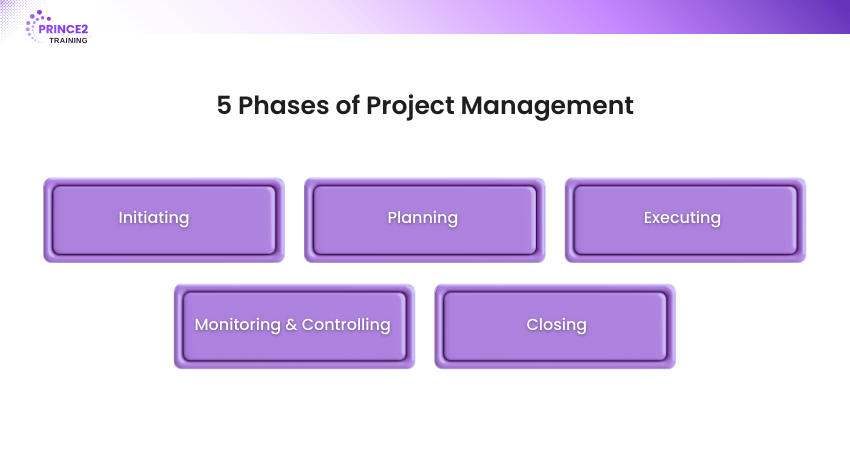
Initiating
1) Define project scope, objectives, and boundaries.
2) Create a high-level overview of resources, timelines, and budgets.
3) Prepare a Project Initiation Document (PID) for larger projects.
Planning
1) Select team members, define deliverables, and estimate resources.
2) Set milestones and deadlines, and choose the Project Management methodology (e.g., Agile, Scrum, Waterfall).
Executing
1) Implement the project plan, manage workflows, and execute tasks.
2) Coordinate with team members and apply corrective measures as needed.
Monitoring & Controlling
1) Regular check-ins to track progress against the plan.
2) Use visual tools (e.g., Kanban Boards, Gantt Charts) for real-time updates and adjustments.
Closing
1) Finalise project deliverables and hand them over to stakeholders.
2) Conclude contracts, conduct a review, and document lessons learned.
Different Project Management Tools
Project Management relies on various tools to stay organised and track progress. Depending on the project's size and complexity, different tools may be needed, while smaller projects might require fewer. Here are the most common tools:
Project Management Software
1) Organises, plans, and tracks project activities.
2) Examples: Microsoft Project, Asana, Trello, Jira.
Communication Tools
1) Enables real-time collaboration.
2) Examples: Slack, Microsoft Teams, Zoom.
Document Management Systems
1) Stores and shares project documents.
2) Examples: SharePoint, Google Drive, DropBox.
Time-Tracking Software
1) Tracks time and expenses.
2) Examples: Harvest, Toggl.
Risk Management Tools
1) Identifies and analyses risks.
2) Examples: Risk Register, Monte Carlo simulations.
Become an expert in Agile Project Management—Join our Scrum Master Training today and lead your team to success!
Tips for Successful Project Management
Proper Project Management is all about striking the right balance between structure and flexibility. These practical tips will help you stay organised and adapt smoothly to changing needs:
1) Start Strong with a Kickoff Meeting: Set clear goals, timelines, and responsibilities to align the team and build early momentum.
2) Identify Task Dependencies: Use visuals like Gantt charts to understand task relationships and prevent delays.
3) Determine the Critical Path: Spot the longest chain of essential tasks to know where deadlines are rigid and where there’s flexibility.
4) Set Realistic Timelines: Refer to past work and allow buffer time to avoid rushed delivery.
5) Use Project Management Tools: Platforms like Jira or Trello centralise communication and reduce scattered updates.
6) Clarify Responsibilities Early: Ensure each team member knows their role to avoid overlap and confusion.
7) Plan Collaboratively: Involving the team leads to more accurate planning and stronger ownership.
8) Stay Adaptable: Be ready to adjust plans as requirements evolve, while keeping the final goal in focus.
Conclusion
Project Management is the art of turning any complex vision into reality. It’s where plans meet purpose, and ideas take flight. Balancing deadlines, resources, and teamwork is a dynamic dance of organisation and adaptation. Whether launching software or building skyscrapers, understanding What is Project Management is the magic behind delivering big dreams on time and within budget.
Unlock the power of process improvement—join our Lean Six Sigma Training and drive efficiency in your projects!
1) What are the Five Key Roles as a Project Manager?
A Project Manager typically takes on five main roles:
1) Leader: Motivates the team
2) Planner: Defines goals and timelines
3) Communicator: Keeps stakeholders aligned
4) Problem Solver: Handles challenges
5) Coordinator: Ensures smooth execution across tasks
2) What Do Project Managers Do?
Project Managers plan, organise and oversee projects from start to finish. They perform the following functions:
1) Define the objectives
2) Assign tasks
3) Manage budgets and timelines
4) Track progress
5) Communicate with stakeholders
6) Ensure the final outcome meets requirements
3) What Skills are Needed in Project Management?
The key skills needed in Project Management include:
1) Leadership
2) Time Management
3) Communication
4) Risk Assessment
5) Problem-solving
6) budget control
7) Adaptability
8) Technical knowledge of tools like Gantt charts, Agile boards or project software
 Contact@prince2training.co.uk
Contact@prince2training.co.uk 01344203999
01344203999





 Back
Back






 Continue Browsing
Continue Browsing
