Table of Content

Projects can get messy fast. One missed deadline, and suddenly everything feels like it’s falling apart. The Critical Path Method in Project Management is your secret weapon for bringing order to chaos. It helps you focus on what matters, manage time better, and deliver projects without last-minute stress.
This blog explains what the Critical Path Method in Project Management is, how to use it, its key components, and the steps to find the critical path. We’ll also cover an example, key benefits, limitations, comparisons with PERT and Gantt Charts, and expert tips for better Project Management.
Table of Contents
1) What is the Critical Path Method (CPM)?
2) How to Use Critical Path Management?
3) Key Components of CPM
4) How to Find a Project's Critical Path?
5) Example of the Critical Path Method
6) Benefits of CPM in Project Management
7) Limitations of CPM in Project Management
8) Comparing CPM vs PERT vs Gantt Charts
9) Tips for Managing Critical Path Method
10) Conclusion
What is the Critical Path Method (CPM)?
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a Project Management technique used to plan and schedule tasks in complex projects. It identifies the longest sequence of dependent activities that determines the shortest time required to complete the project. If any task on this path is delayed, the whole project gets delayed, so Project Managers focus on these tasks to complete the project on time.
Using the Critical Path Method in Project Management makes handling projects much easier. It builds on the idea of identifying the most important tasks, helping you use resources wisely and finish work on time. It also gives a clear view of the entire project, allowing you to spot problems early and prevent delays.
How to Use Critical Path Management?
To use the Critical Path Method (CPM), list tasks, set dependencies and durations, create a network diagram, and find start and finish times. This helps plan well, manage resources, track progress, and complete projects on time. Here are the main ways CPM makes Project Management easier:
1) Project Planning: Map out tasks and dependencies
2) Time Estimation: Calculate the total project duration
3) Resource Allocation: Allocate the exact resources to the most important tasks
4) Tracking Progress: Monitor critical tasks to avoid delays
5) Improving Efficiency: Identify where adjustments are needed to save time
Key Components of CPM
To understand CPM better, you need to know its main components.
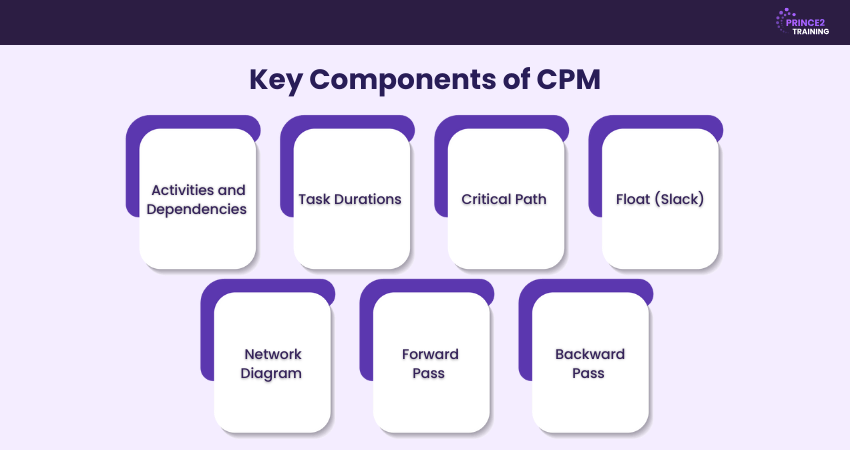
1) Activities and Dependencies
Projects are made up of different tasks, also called activities. In CPM, it’s important to know how these activities are connected. Some jobs have to be done before they can start, but some can be done at the same time.
2) Task Durations
Every task has a specific amount of time needed to complete it, known as its duration. Estimating durations correctly is important to create a realistic project schedule.
3) Critical Path
The critical path is the longest chain of dependent tasks that determines the shortest time needed to finish a project. If any task on this path gets delayed, the entire project will be delayed.
4) Float (Slack)
Float, also called slack, is the extra time a task can be late without affecting the overall project deadline. Assignments on the critical path have zero float, while others may have some flexibility.
5) Network Diagram
A network diagram is a visual chart showing all the project tasks and how they are connected. It uses boxes or circles for tasks and arrows to show their order and dependencies.
6) Forward Pass
The forward pass is used to find the earliest start and earliest finish times for each task. It calculates the minimum time required to complete the project by moving from the start to the end.
7) Backward Pass
The backward pass calculates the latest start and latest finish times for each task without delaying the project. It works from the project’s end back to the start to find tasks that have flexibility and those that don’t.
Learn core Project Management in just one day with our Introduction to Project Management Training – Join now!
How to Find a Project's Critical Path?
The Critical Path Method (CPM) helps Project Managers find the longest sequence of dependent tasks that shows the minimum time to finish a project. Knowing the critical path lets you focus on tasks that cannot be delayed without affecting the deadline. Here are the steps to find it:
Step 1: List all Project Tasks
Write down every task required to complete the project. This gives a clear picture of all the work involved.
Step 2: Define Task Sequence
Arrange tasks in the correct order and identify dependencies. Some tasks have to be done before they can begin, while others can be done at the same time.
Step 3: Estimate Task Durations
Assign an estimated duration for each task. Accurate time estimates are essential to create a realistic project schedule.
Step 4: Create a Network Diagram
Draw a visual diagram to show all tasks, their durations, and dependencies. This helps in understanding the workflow clearly.
Step 5: Determine the Critical Path
Find the longest sequence of dependent tasks through the network diagram. This is the critical path, any delay in these tasks will delay the whole project.
Step 6: Calculate Float
Check for tasks that have extra time or float. Tasks on the critical path have zero float, while others may allow some flexibility without affecting deadlines.
Step 7: Track and Monitor Progress
Once the critical path is identified, monitor these tasks closely. Keep updating the schedule regularly to manage delays and stay on track.
Build your Agile Project Management skills fast with our PRINCE2 Agile® Foundation Training – Register today!
Example of the Critical Path Method
The Critical Path Method (CPM) helps find the longest chain of tasks that determines how long a project will take. Let’s see an example:
Assume that you are working on a website project. These are the tasks:
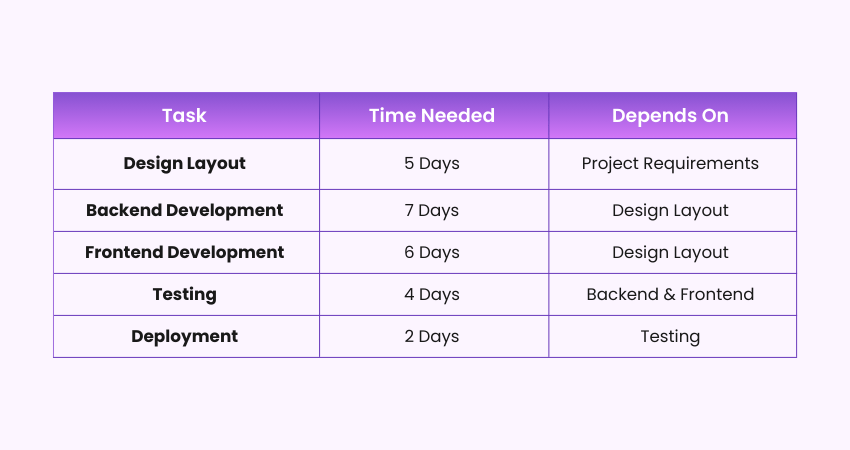
Path 1: Design, Backend, Testing, Deployment = 18 days
Path 2: Design, Frontend, Testing, Deployment = 17 days
The longest path is 18 days, so this is the critical path.
This means that if any task on this path is delayed, the whole project will also be delayed. CPM helps Project Managers focus on these important tasks and complete the project on time.
Benefits of CPM in Project Management
The Critical Path Method (CPM) makes Project Management easier and more organised. It helps Project Managers focus on important tasks, reduce risks, and finish projects on time. Here are the key benefits:
1) Identifying Critical Activities
CPM helps you find the most important tasks that directly affect the project’s completion time. By knowing which tasks cannot be delayed, you can focus your efforts and manage them closely to keep the project on track.
2) Risk Evaluation
CPM shows task dependencies clearly, making it easier to spot risks early. When you know how tasks are linked, you can plan better, adjust schedules, and solve problems before they affect the project.
3) Accurate Timelines
With CPM, you can create a realistic project schedule by understanding which tasks take more time and which can be shortened. It highlights the sequence and duration of tasks, helping you complete the project faster when needed.
4) Task Prioritisation
CPM shows you which tasks need your attention first. Tasks on the critical path have the highest priority because any delay in them delays the whole project. This helps you allocate resources wisely and avoid missed deadlines.
5) Improved Clarity
CPM uses visual diagrams that give a clear picture of the entire project. You can easily see how tasks are connected, understand dependencies, and identify areas where resources are needed if delays happen.

Limitations of CPM in Project Management
The Critical Path Method (CPM) has limits, including fixed task durations, complexity in large projects, no Resource Management, and less flexibility. Let’s look at these limitations in detail:
1) Complexity
Using CPM can be difficult for large projects with many tasks and dependencies. Calculations for the critical path and float can take a lot of time and effort. It often requires careful planning and constant monitoring to manage everything effectively.
2) Limited Applicability in Some Projects
CPM works best when tasks are clear, durations are predictable, and dependencies are fixed. It may be less effective for dynamic projects that evolve frequently, such as Agile software development.
3) Overemphasis on the Critical Path
Since CPM focuses on the critical path, tasks with extra time or float may get less attention. Ignoring these tasks can sometimes cause delays or poor resource use. It’s important to monitor all tasks to keep the project running smoothly.
4) Estimation Inaccuracies
CPM relies on accurate time estimates for each task. If these estimates are wrong, the critical path may be incorrect, which can lead to delays and poor planning. Taking time to review and update estimates can help improve accuracy and avoid problems.
5) Software Reliance
Many Project Management tools automate CPM calculations, which makes the process easier. However, depending only on software can limit your understanding of CPM. Knowing the basics is important for making better project decisions.
Boost your project expertise and agility with our PRINCE2 Agile® Practitioner Training – Join now!
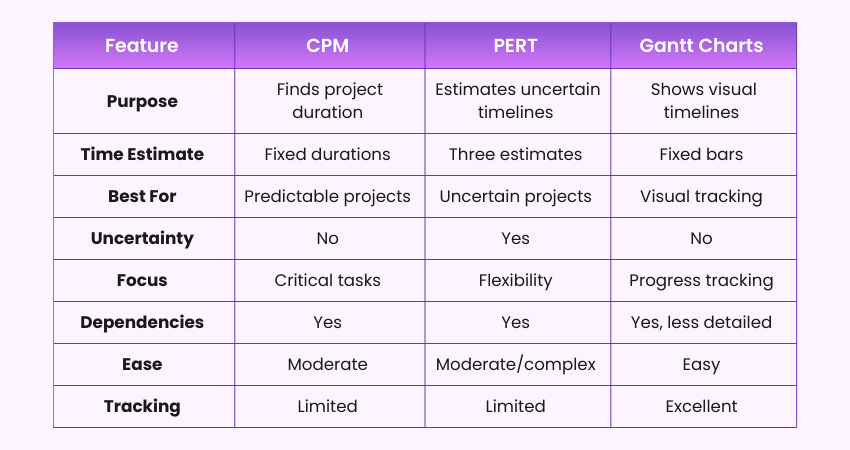
Comparing CPM vs PERT vs Gantt Charts
The Critical Path Method (CPM), Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT), and Gantt charts are all Project Management tools. Here is the comparison between CPM vs PERT vs Gantt Charts:
Tips for Managing Critical Path Method
Here are some tips to manage the Critical Path Method (CPM) easily:
1) Define the Project and Tasks: Be clear about the project scope and list all tasks.
2) Give Realistic Time Estimates: Set practical timelines to avoid delays.
3) Identify Task Dependencies: Understand which tasks depend on others and make a network diagram.
4) Do Forward and Backwards Passes: Find the earliest and latest start and finish times to know the critical path.
5) Use Gantt Charts: Show timelines, task order, and progress in a simple visual way.
6) Check and Update Regularly: Keep track of progress and make changes when needed.
7) Communicate with Stakeholders: Keep everyone informed about updates and delays.
8) Manage Risks Early: Spot possible problems and prepare backup plans.
9) Use Project Management Tools: Tools like MS Project, Asana, or Wrike make tracking and teamwork easier.
Conclusion
The Critical Path Method in Project Management is a powerful way to plan, schedule, and manage tasks effectively. It helps identify important activities, allocate resources wisely, and avoid delays. By focusing on the critical path and updating schedules regularly, Project Managers can improve efficiency, reduce risks, and make sure projects are completed on time and within scope.
Secure your future in Project Management with our PRINCE2 Training – Join now!
 info@theknowledgeacademy.com
info@theknowledgeacademy.com 01344203999
01344203999





 Back
Back







 Continue Browsing
Continue Browsing
